SQL DELETE Statement
SQL DELETE is a basic SQL operation used to delete data in a database. SQL DELETE is an important part of database management DELETE can be used to selectively remove records from a database table based on certain conditions. This SQL DELETE operation is important for database size management, data accuracy, and integrity.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE some_condition;
Parameter Explanation:
-
Some_condition: condition to choose a particular record.
-
table_name: name of the table
Note
We can delete single as well as multiple records depending on the condition we provide in the WHERE clause. If we omit the WHERE clause then all of the records will be deleted and the table will be empty.
The sample table is as follows GFG_Employees:
Query:
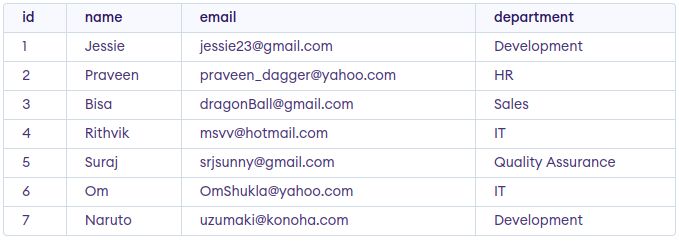
Assume we have created a table named GFG_Employee which contains the personal details of the Employee including their id, name, email and department etc. as shown below
CREATE TABLE GFG_Employees (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR (20) ,
email VARCHAR (25),
department VARCHAR(20)
);
INSERT INTO GFG_Employees (id, name, email, department) VALUES
(1, 'Jessie', '[email protected]', 'Development'),
(2, 'Praveen', '[email protected]', 'HR'),
(3, 'Bisa', '[email protected]', 'Sales'),
(4, 'Rithvik', '[email protected]', 'IT'),
(5, 'Suraj', '[email protected]', 'Quality Assurance'),
(6, 'Om', '[email protected]', 'IT'),
(7, 'Naruto', '[email protected]', 'Development');
SELECT * FROM GFG_Employees;
Output:
Deleting Single Record
You can delete the records named Rithvik by using the below query:
Query:
DELETE FROM GFG_Employees WHERE NAME = 'Rithvik';
Output:

Deleting Multiple Records
Delete the rows from the table GFG_Employees where the department is “Development”. This will delete 2 rows(the first row and the seventh row).
Query:
DELETE FROM GFG_Employees WHERE department = 'Development';
Output:

Delete All of the Records
To remove all the entries from the table, you can use the following query:
Query:
DELETE FROM GFG_EMPLOyees;
OR
DELETE * FROM GFG_EMPLOyees;
Output:
All of the records in the table will be deleted, there are no records left to display. The table GFG_EMPLOyees will become empty.

Note
DELETE is a DML (Data Manipulation Language) command, the operation performed by DELETE can be rolled back or undone by using the COMMIT or ROLLBACK command.
Conclusion
Existing records in a table can be deleted using the SQL DELETE Statement. We can delete a single record or multiple records depending on the condition we specify in the WHERE clause and With DELETE statement, you can filter the uncommitted records from the table.