Docker – Compose
An open-source platform called Docker makes it simple to design, ship, and deploy applications. It runs an application in an isolated environment by compiling all of its dependencies into a so-called container. for additional information on Docker. In a normal case, a number of services, such as a database and load balancing, are required to support an application. We’ll look at Docker Compose assistance with setting up many services in this article. Also, we will see a demonstration of installing and utilizing Docker Compose.
What is Docker Compose ?
Docker Compose will execute a YAML-based multi-container application. The YAML file consists of all configurations needed to deploy containers Docker Compose, which is integrated with Docker Swarm, and provides directions for building and deploying containers. With Docker Compose, each container is constructed to run on a single host.
Docker Compose simplifies the management of multi-container Docker applications. If you’re looking to master Docker Compose and its role in the larger DevOps lifecycle, the DevOps Engineering – Planning to Production course offers hands-on examples of managing multi-container applications
Install Docker Compose
We can run Docker Compose on macOS, Widows, and 64-bit Linux.
-
For any significant activity, Docker Compose depends on Docker Engine. Depending on your arrangement, we must ensure that Docker Engine is installed either locally or remotely.
-
A desktop system such as Docker for Mac and Windows comes with Docker Compose preinstalled.
-
Install Docker first as instructed in Docker installation on the Linux system before beginning the installation of Docker Compose.
How to Install Docker Compose on Ubuntu ? A Step-By-Step Guide
Step 1: Update the package Manager
The following scripts will install the most recent version of Docker Compose and update the package management.
sudo apt-get update
Step 2: Download the Software
Here we are using the Ubuntu flavor in the Linux Operating system. So the package manager is “apt-get” If you want to install it in Redhat Linux then the package manager will be “yum”.
Step 3: Apply Permissions
Apply the Executable permissions to the software with the following commands:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Step 4: Verify the Download Software
Verify whether the docker compose is successfully installed or not with the following command:
docker-compose --version
Docker Container
A docker container is a lightweight Linux-based system that packages all the libraries and dependencies of an application, prebuilt and ready to be executed. It is an isolated running image that makes the application feel like the whole system is dedicated to it. Many large organizations are moving towards containers from VMs as they are light and simple to use and maintain. But when it comes to using containers for real-world applications, usually one container is not sufficient. For example, Let’s assume Netflix uses a microservices architecture. Then it needs services for authentication, Login, Database, Payment, etc., and for each of these services, we want to run a separate container. It is preferred for a container to have only a single purpose.
Now, imagine writing separate docker files, and managing configuration and networks for each container. This is where Docker Compose comes into the picture and makes our lives easy.
Why Docker Compose ?
As discussed earlier, a real-world application has a separate container for each of its services. And we know that each container needs to have a Dockerfile. It means we will have to write maybe hundreds of docker files and then manage everything about the containers individually, That’s cumbersome.
Hence, we use docker-compose, which is a tool that helps in the definition and running of multi-container applications. With the help of Docker Compose you can start and stop the services by using its YAML file. Docker-compose allows us to start and stop all the services with just a few simple commands and a single YAML file for each configuration.
In contrast to utilizing a prebuilt image from Docker Hub, which you may configure with the docker-compose.yaml file, if you are using a custom image, you will need to declare its configurations in a separate Dockerfile. These are the features that docker-compose support:
-
All the services are isolated running on a single host.
-
Containers are recreated only when there is some change.
-
The volume data is not reset when creating new containers, volumes are preserved.
-
Movement of variables and composition within environments.
-
It creates a virtual network for easy interaction within the environments.
Now, let’s see how we can use docker-compose, using a simple project.
How to Use Docker Compose ?
In this project, we will create a straightforward Restfull API that will return a list of fruits. We will use a flask for this purpose. And a PHP application will request this service and show it in the browser. Both services will run in their own containers.
-
First, Create a separate directory for our complete project. Use the following command.
mkdir dockerComposeProject -
Move inside the directory.
cd dockerComposeProject
Step 1: Create API
We will create a custom image that will use Python to serve our Restful API defined below. Then the service will be further configured using a Dockerfile.
Then create a subdirectory for the service we will name it product. and move into the same.
mkdir product
cd product
Step 2: Build Python api.py
The following is the python file that helps in making an API call:
Create a Dockerfile to define the container in which the above API will run.
from flask import Flask
from flask_restful import Resource, Api
# create a flask object
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
# creating a class for Fruits that will hold
# the accessors
class Fruits(Resource):
def get(self):
# returns a dictionary with fruits
return {
'fruits': ['Mango', 'Pomegranate', 'Orange', 'Litchi']
}
# adds the resources at the root route
api.add_resource(Fruits, '/')
# if this file is being executed then run the service
if __name__ == '__main__':
# run the service
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80, debug=True)
Step 3: Create requirements.txt
flask
flask-restful
Step 4: Create Dockerfile For Python API
FROM python:3
COPY . /usr/src/app
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
CMD ["python", "api.py"]
FROM accepts an image name and a version that the docker will download from the docker hub. The current working directory’s contents can be copied to the location where the server expects the code to be by using the copy command. Moreover, the CMD command takes a list of commands to start the service once the container has been started.
Step 5: Create Php HTML Website
Let’s create a simple website using PHP that will use our API.
Move to the parent directory and create another subdirectory for the website.
cd ..
mkdir website
cd website
index.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Fruit Service</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to India's Fruit Shop</h1>
<ul>
<?php
$json = file_get_contents('http://fruit-service');
$obj = json_decode($json);
$fruits = $obj->fruits;
foreach ($fruits as $fruit){
echo "<li>$fruit</li>";
}
?>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
Now create a compose file where we will define and configure the two services, API and the website.
Move out of the website subdirectory using the following code.
cd ..
And then create the file name as . docker-compose.yaml
Step 6: Create Docker-compose.yaml file
The following is the sample docker compose file code:
version: "3"
services:
fruit-service:
build: ./product
volumes:
- ./product:/usr/src/app
ports:
- 5001:80
website:
image: php:apache
volumes:
- ./website:/var/www/html
ports:
- 5000:80
depends_on:
- fruit-service
Docker-compose.yaml file Explanation
The first line is optional where we specify the version of the docker-compose tool. Next services define a list of services that our application is going to use. The first service is fruit service which is our API and the second one is our website. The fruit service has a property build that contains the dockerfile that is to be built and created as an image. Volumes define storage mapping between the host and the container so that we can make live changes. Finally, port property exposes the containers port 80 through the host’s 5001.
The website service does not use a custom image but we download the PHP image from the Docker hub and then map the websites folder that contains our index.php to /var/www/html (PHP expects the code to be at this location). Ports expose the container port. Finally, the depends_on specifies all the services on which the current service depends.
The folder structure after creating all the required files and directory will be as follows:
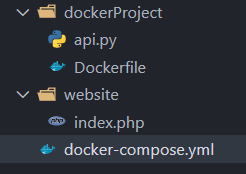
Run the application stack with Docker Compose
Now that we have our docker-compose.yml file, we can run it.
To start the application, enter the following command.
docker-compose up -d
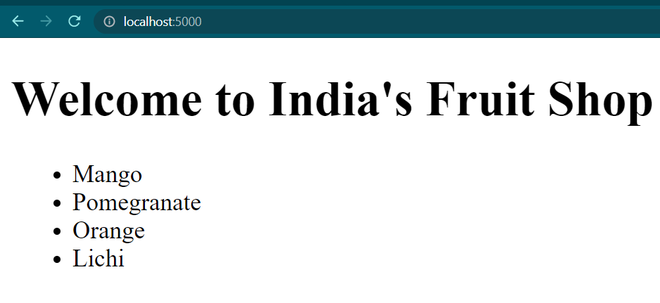
Now all the services will start and our website will be ready to be used at localhost:5000.
Open your browser and enter localhost:5000.
Output
To stop the application, either press CTRL + C or
docker-compose stop
Advantages of Docker Compose
The following are the advantages of Docker Compose:
-
Simplifies Multi-Container Management: Docker Compose facilitates with features such as define, configure, and run multiple containers with a single YAML file, streamlining the management of complex applications.
-
Facilitates Environment Consistency: It facilitates with the development, testing, and production environments that are consistent with reducing the risk of environment-related issues.
-
Automates Multi-Container Workflows: With Docker Compose, you can easily automate the setup and teardown of multi-container environments, making it ideal for CI/CD pipelines and development workflows.
-
Efficient Resource Management: It enables efficient allocation and management of resources across multiple containers, improving application performance and scalability.
Disadvantages of Docker Compose
The following are the disadvantages of Docker Compose:
-
Limited Scalability: Docker Compose is not developed for large scaling mechanism which can limit its effectiveness for managing complex deployments.
-
Single Host Limitation: Docker Compose will operate on a single host, making it unsuitable for distributed applications with requiring multi-host orchestration.
-
Basic Load Balancing: It lacks with advanced load balancing and auto-scaling features found in more robust orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
-
Less Robust Monitoring: Docker Compose provides minimal built-in monitoring and logging capabilities compared to more comprehensive solutions.
Features of Docker Compose
The following are the features of Docker Compose:
-
Multi-Container Deployment: it facilitates with easily define and run applications with multiple containers using a single YAML file.
-
Service Isolation: Each service runs in its own container, with ensuring the isolation and reducing conflicts between services.
-
Simplified Configuration: It helps in centralizing all the configurations, including networking, volumes, and dependencies, in the docker-compose.yml file.
-
Scalability: It provides the effortlessly scaling of services up or down with a single command, allowing for flexible and dynamic resource management.
Best Practices of Docker Compose
The following are some of the best practices of Docker Compose:
-
Use Environment Variables: It is suggestible to store configuration values and secrets in environment variables to keep your docker-compose.yml clean and secure.
-
Keep Services Lightweight: It is preferred to design each service to handle a single responsibility to ensure modularity and ease of maintenance.
-
Leverage Volumes: Usage of volumes with enhancing in maintaining the persistent data storage, allowing data to persist across container restarts and updates.
-
Version Control Your Compose Files: It is preferred to maintain your docker-compose.yml file in version control (e.g., Git) to track changes and collaborate with your team effectively.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about Docker Compose, and why and when to use it. And demonstrated its usuage through a simple project. It helps in automating the creating process of containers through services, networks and volumes with through respective keywords availability. Through using docker compose management and automation of containers and its volumes, networks will be easier.