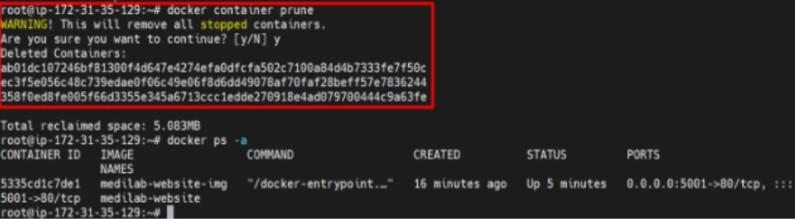
Remove All Containers and Images in Docker
In Docker , if we have exited a container without stopping it, we then need to stop them manually as it has not stopped on exit. Similarly, for images, we need to delete them from top to bottom as some containers or images might be dependent on the base images, we can any time download the base image at. So it is a good idea to delete unwanted or dangling images from the current machine.
How To Delete The Images in Docker ?
Remove Image
To delete the image by the ImageId/Name we can use the following command. To know more about how to build a docker image with the help of Dockerfile refer to Concept of Dockerfile.
docker rmi <imageId/Name>
Force Remove Image
To force remove the docker Images by the ImageID/Name we can use the following command.
docker rmi -f <imageId/Name>
Note
We can’t remove the images by force or normally while the container is running.
Dangling Images
Dangling Images are those that don’t map to either the repository or the tag. The command used is to remove the dangling images. To know more about how to tag Docker images by referring to Docker image tags.
docker image prune
Removing all Images
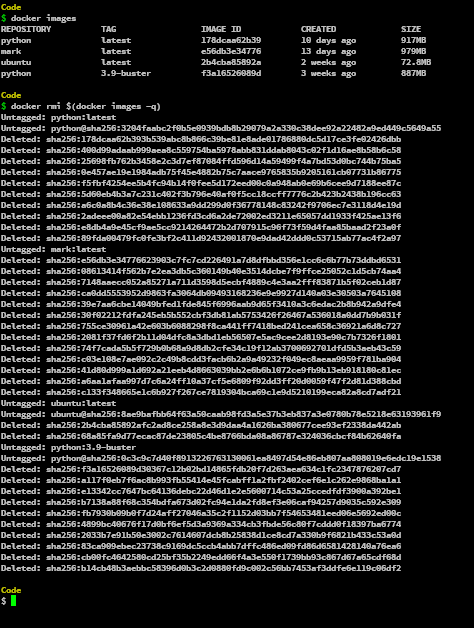
We can remove all images in the docker-machine to remove unwanted clutter and space in the system. We can anyway fetch the latest version or specific versioned image from the docker registry or from the cache.
docker rmi $(docker images -q)
How To Delete Containers In Docker
Before deleting the containers we need to stop the container first for that we use the command.
docker stop <containerId/Name>
The Difference Between Docker Stop & Docker Kill
Docker stop will first send a SIGTERM signal before killing the process with a SIGKILL signal and a grace period. When Docker kill sends SIGKILL, it immediately terminates the process.
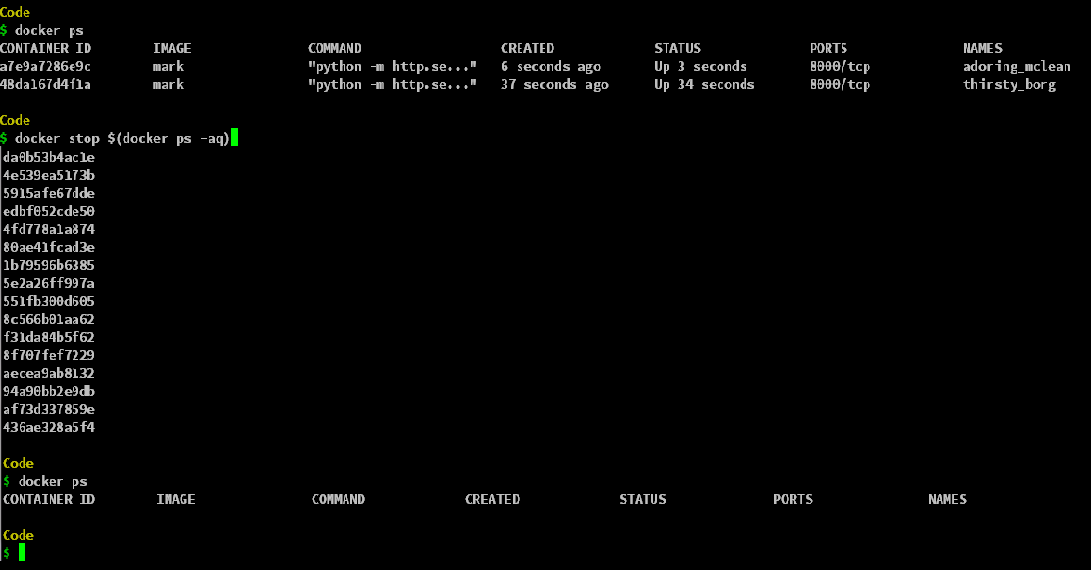
Stop all running Containers: In order to stop the containers which have not exited. This might happen when the command used in the Docker image is left running. The command should be exited and this will in turn stop the container. To stop the container when you have not exited the container by stopping the command, you need to run the following command.
docker stop $(docker ps -aq)
Delete The Container: If the container is stopped then we can use the following command to delete the container.
docker rm <containerId/Name>
Force Delete The Container: We can force remove the containers while they are running without stopping them by using the below command.
docker rm -f <containerId/Name>
Remove all Containers
To remove all containers from the docker machine, we need to get the ids of all the containers. We can simply get the ids of the containers with the command docker ps -aq , then by using the docker rm command, we can remove all the containers in the docker-machine.
docker rm $(docker ps -aq)

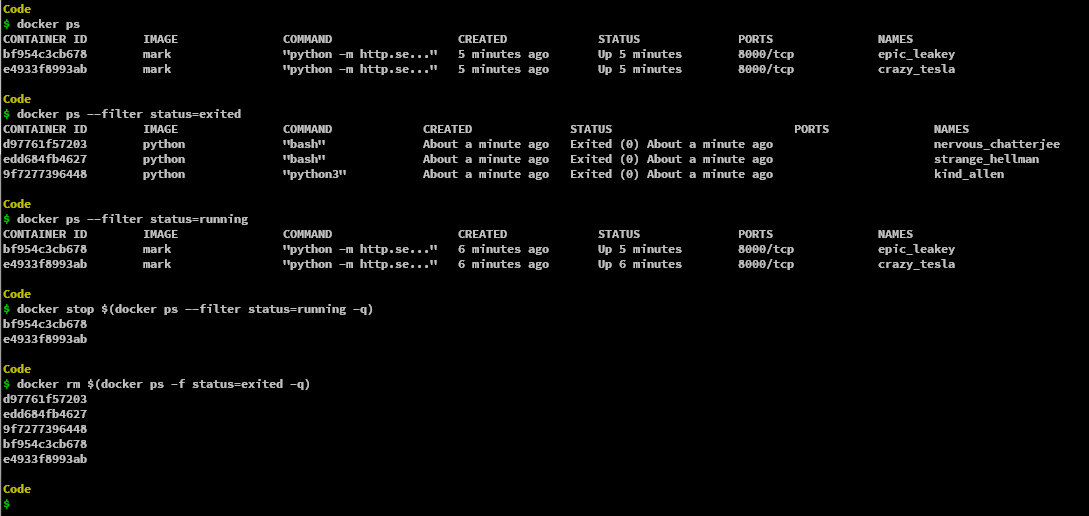
Remove all Stopped Containers
To remove all containers which are stopped/exited, we can use filters in the ps command argument. We can’t directly remove a container if it is not stopped. We can stop containers that are not exists or are running by using the -f argument to the ps command in docker, the -f or –filter option takes in a filter like status=exited or status=running or name and so on. We can filter out to stop the specific containers according to the requirement.
docker rm $(docker ps -aq --filter status="exited")
After filtering out the container which is running, we can use the stop command to stop those containers with the -q to silence the numeric ids associated with those containers.
docker stop $(docker ps --filter status=running -q)
This will stop all the containers, and thus we can now remove the containers from the docker-machine. We can even filter the containers which are stopped here to remove only those whose status is exited.
docker rm $(docker ps --filter status=exited -q)
The below command removed all the containers which are in the existing state. That means the containers stopped.
docker container prune