How to Install Docker using Chocolatey on Windows ?
Installing Docker in Windows with just the CLI is quite easier than you would expect. It just requires a few commands. This article assumes you have chocolatey installed on your respective windows machine. If not, you can install chocolatey from here. Chocolatey is a package manager for the Windows Operating system.
Installing Docker using Chocolatey on Windows
After installing chocolatey, you can verify your installation by running the command on a new CMD or a Powershell instance.
choco --v
If the following command gives a version number then you have installed Chocolatey successfully on Windows.
PS C:\Users\Admin> choco --v
Chocolatey v0.12.1
It should not be exactly that the version number will be different as per your time of installing the chocolatey on your system.
Installing Docker
After installing chocolatey in our Windows System, we need to install the docker package from the chocolatey package manager. To do that we need to simply run the following command in a CMD or a PowerShell instance.
choco install docker
If you want a specific version of docker you can pass the following argument to the command:
choco install docker --version 17.05.0
So, after this docker is installed, we need to install the docker-daemon using a docker machine to actually install and work with images and containers.
Understanding Docker installation and configuration is the first step to mastering container management.
To dive deeper into Docker setups and configurations, particularly on Windows, the DevOps Live Course provides practical guidance on Docker installations and its integration with CI/CD pipelines.
Installing Docker-Machine
To install docker-machine with chocolatey we can run the simple command as follows:
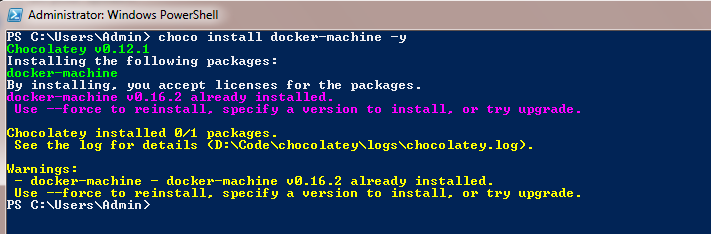
choco install docker-machine -y
It will take some time to install the docker-machine package on your local machine.
Installing Virtual Box
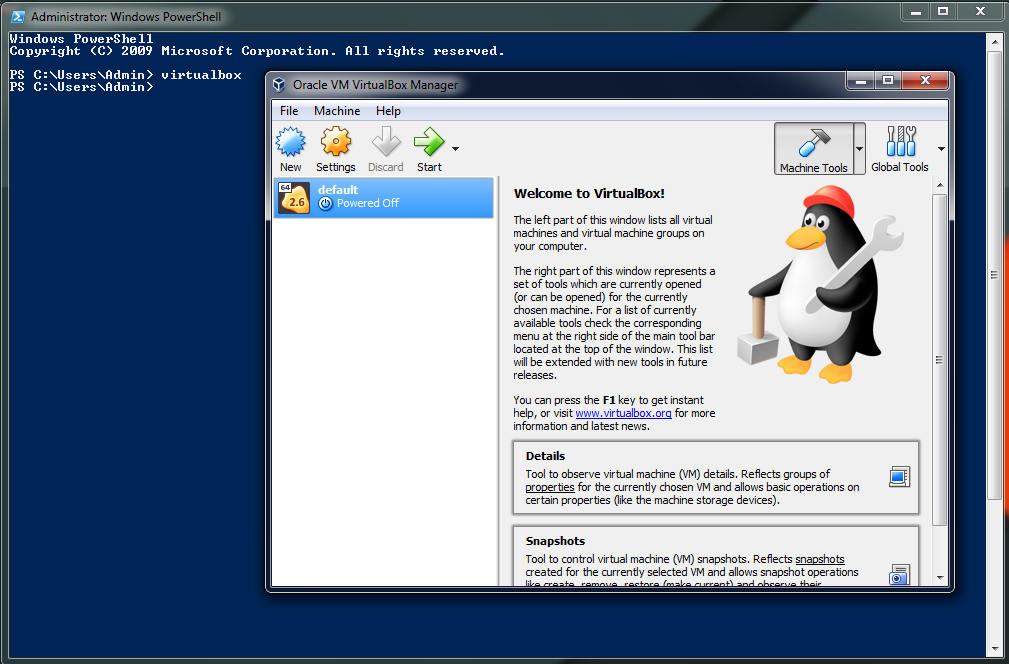
Installing Virtual Box along with VTx setup. Virtual Box is a virtual machine manager, you can basically create virtual machines in your Primary Operating System which here is Windows. You can install Virtual Box on Windows from the official website of Oracle.
Also, add the path of Virtual Box installation to the environment variable PATH. You can add the PATH of the Virtual Box using a CMD or a PowerShell.
set PATH=%PATH%;"C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox"
You need to add the Virtual Box system permanently in the system, you need to add it to an environment variable PATH by clicking on Control Panel -> Advanced System Settings -> Environment Variables -> Edit Path variable and simply add the path and save the variable.
The Path can be surely different as per your installation preferences. This will add Virtual box binaries as a PATH to be run from CMD or PowerShell instances in Windows. So, after we run VirtualBox in CMD or PowerShell, we get the GUI.
Now, we need to enable VTx Setting in your System BIOS. This can be checked and enabled by pressing certain specific keys like F2 or F10 or others at the boot-up time of the system.
Creating a Default Docker Machine
Now, after we have installed Virtual Box and Docker machine, we can move on to creating a default docker machine on the system.
docker-machine create --driver virtualbox default
If it gives an error of enabling the VTx in BIOS, enter the check for it by re-running the command as follows:
docker-machine create -d virtualbox --virtualbox-no-vtx-check default
Starting Docker Machine
After this, it will create the default docker machine in the system. We now can invoke the docker machine and configure the machine to run the docker engine.
We need to run the command:
docker-machine start
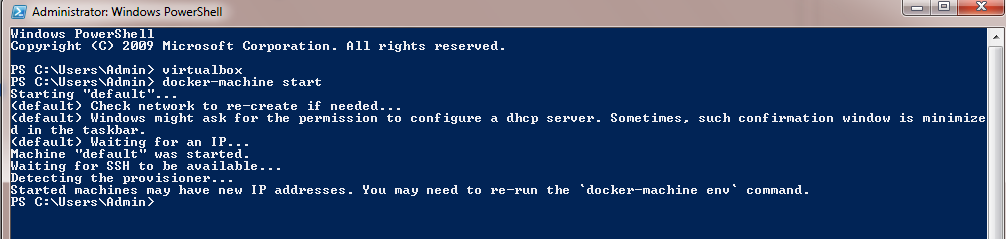
This will start the default docker-machine which is a virtual machine created in a virtual box. After finishing the command the prompt itself says to run the env command. so, we need to run the command as follows:
docker-machine env default | Invoke-Expression
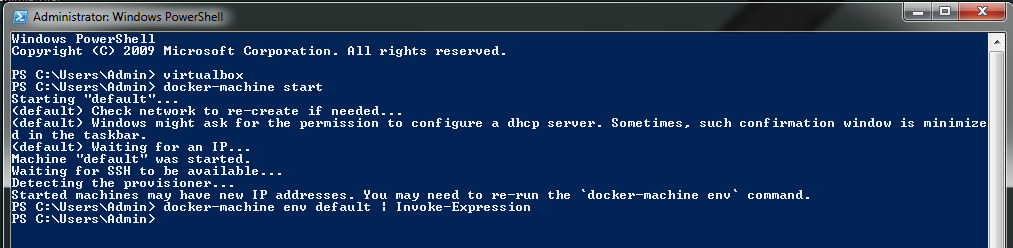
This will finally start the docker-machine in the system, which means the docker daemon is running in your system now. We can finally run install or run docker in CMD or PowerShell instances.
Running Docker
So, to run docker we can follow the official docker documentation.
docker run hello-world
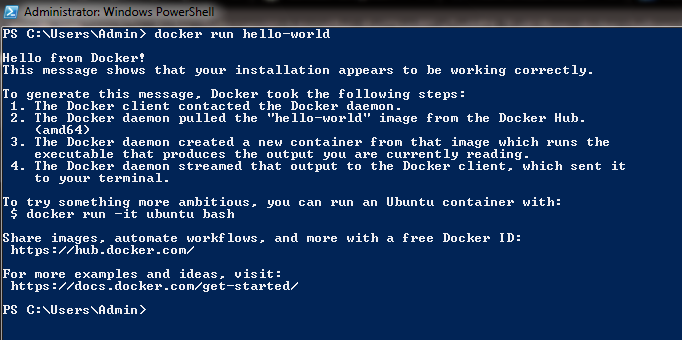
Now, we finally have a docker setup in Windows using the chocolatey package manager. You can now use docker as you wished to do by running or pulling images and containers.
Stopping Docker Machine
Before you shut down the system, you need to stop the docker-machine so it doesn’t lag while shutting down. So, run the following simple command to stop the docker machine.
docker-machine stop
So, from this article, we were able to set up Docker using a chocolatey package manager in Windows.
Are you ready to unleash the power of DevOps to streamline your Software Development and Deployment? Learn about our DevOps Live Course at GeeksforGeeks, created for all professionals in practice with continuous integration, delivery, and deployment. Learn about leading tools, industry best practices, and techniques for automation through an interactive session with hands-on live projects. Whether you are new to DevOps or looking to improve your skills, this course equips you with everything needed to streamline workflows and deliver excellent quality software in the least amount of time. Learn to take your skills in DevOps to the next level now, and harness the power of streamlined software development!