How to use Docker Default Bridge Networking ?
Docker allows you to create dedicated channels between multiple Docker Containers to create a network of Containers that can share files and other resources. This is called Docker Networking. You can create Docker Networks with various kinds of Network Drivers which include Bridge drivers, McVLAN drivers, etc. By default, if you do not mention a driver while creating a network, it automatically chooses the default bridge driver. Bridge drivers are single-host networking drivers and hence their scope is limited to local.
In this article, we are going to discuss how to create, manage, and use Docker Bridge Networks. For this, you would need a Linux-based Host machine with access to Docker. Without any further ado, let’s dive deep into Docker Bridged Networking.
Bridge Network Driver
The bridge is a default network where containers will be created by default if you are not mentioned any network while creating. The containers which are deployed in the same network can talk to each other the containers which are not in the same network can’t communicate with each other without proper mentions and permissions. While creating a docker network if you are not going to create or mention any network while creating a container. To list the networks in docker you can use the following command.
docker network ls
Types of Docker Networks
There are three main default networks as mentioned following and also to know more about Docker networking refer to Docker Networking.
-
Bridge(default)
-
Host
-
None/Null
Connect a Container To a User-Defined Bridge
If containers are created in a default bridge network. Communication will happen only with the IP Address of the container. Communication will not happen using containerName(hostName). To Check Go inside java web app container and ping maven web app container using name & IP. When we ping using ip it will work it will not be able to communicate using the name.Developers should not code the connectivity based on the IP in case of containers. Since the IP address of containers will be dynamic.IP will keep changing.
To Create Custom Bridge Network
To create a Custom Bridge Network, we can use docker network command, the syntax of this as follows:
docker network create -d <driver> <networkName>
How to create Custom Bridge Network ? A Step-By-Step Guide
The following are the steps that guides you in creating a custom bridge network:
Step 1: Ensure Docker is Running
- The following helps in checking the docker running status:
sudo systemctl status docker
- The following command helps in enabling the docker service:
sudo systemctl enable docker --now
Step 2: Create Bridge Network
- Firstly check the existing networks list with the following command:
docker network ls
- Use the following command to create a new bridge network:
docker network create --driver bridge mynetwork
Step 3: Verify the Network Creation
Use the following command to verify whether the network is successfully created or not:
docker network ls
Step 4: Inspect the Bridge Network
Inspect the created custom bridge networks by using the following command.
docker network inspect mynetwork
If containers are created in custom bridge network. Each container can access other using containerName/ContainerIP.Delete Containers which are running in default bridge or create container with different name.
The Default Bridge Network
Every installation of Docker provides a pre-built default Bridge Network with a Bridge driver scoped locally. You can verify the same using the network ls to know more commands refer to command.Docker – Instruction Commands.
sudo docker network ls
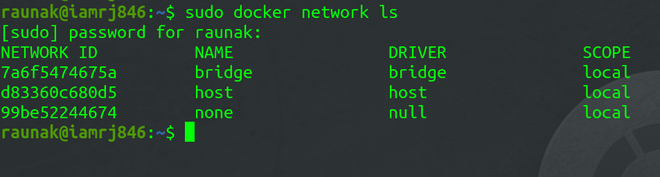
Bridge Driver always provides single-host networking hence, the scope is local.
Connecting A Docker Container In Bridge Network
Note that the Bridge Network we saw in the previous step is the default network for Docker Containers. If you don’t specify any other network, all new Containers will be joined to this default network. To connect an Ubuntu Container to the default bridge network, use this command.
sudo docker run -dt ubuntu

Inspecting The Bridge Network
After you have created the Docker Container, check whether it is running or not.
sudo docker container ls

Since the Container is already running, we can now use the network inspect command to inspect the Docker default bridge network.
sudo docker network inspect bridge
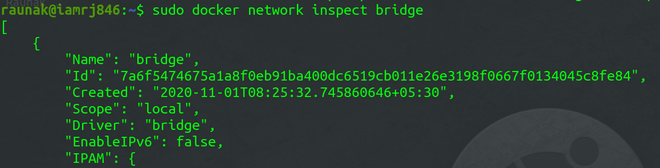
You can see the details related to the Bridge Network in JSON format. You can also check the Containers associated with the network in the Container object.
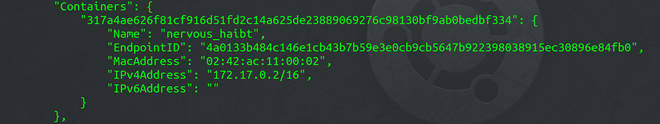
Testing The Network Connectivity
To test the network connectivity, note down the IP address of the Container. In this example, the IP address is “172.17.0.2/16”.We will ping this address from the Docker Host to check the connectivity.
ping 172.17.0.2
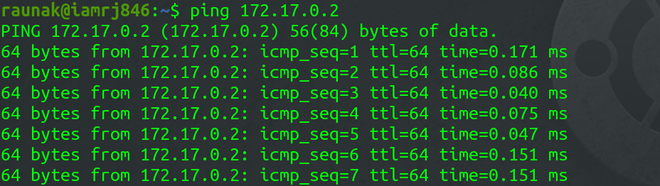
It shows that the host is able to ping the Docker Container in the network.
Differences Between User-Defined Bridges And The Default Bridge
| Feature | Default Bridge Network | User-Defined Bridges Network |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Acts as basic network isolation for containers deployed in this network | Allows creation of custom networks with more configuration policies |
| Communication | Containers communicate using IP addresses | Containers communicate using container names |
| Host Communication | Communication with the host system uses host IP addresses | Communication with the host system uses host IP addresses |
| DNS | Containers use embedded DNS for communication to the internet via DNS resolution | Containers use embedded DNS for communication to the internet via DNS resolution |
Difference between Docker Network Host and Bridge
The following are the difference between docker network host and bridge:
| Feature | Host Network | Bridge Network |
|---|---|---|
| Network Isolation | Shares the host’s network stack, providing no network isolation | Provides a private internal network, isolating containers from the host network |
| Performance | Offers better network performance due to direct use of the host’s network | Slightly lower performance due to the overhead of network bridging |
| Use Case | Suitable for applications needing direct access to the host network, like monitoring tools | Ideal for typical containerized applications needing isolation and controlled communication |
| IP Addressing | Containers use the host’s IP address and ports, leading to potential conflicts | Containers get their own IP addresses within the bridge network, avoiding conflicts with the host |
Difference between Docker network bridge and Overlay
The following are the between docker network bridge and overlay:
| Aspect | Bridge Network | Overlay Network |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Limited to a single host | Spans multiple hosts |
| Use Case | Ideal for simple, local container communication | Suitable for distributed, multi-host environments |
| Configuration | Easy to set up with minimal configuration | Requires more complex setup, often involving a key-value store (like etcd) |
| Performance | Generally faster due to local scope | Slightly slower due to cross-host communication overhead |