Introduction to Docker Swarm Mode
Docker swarm is a container orchestration tool. Swarm Mode in Docker was introduced in version 1.12 which enables the ability to deploy multiple containers on multiple Docker hosts. For this Docker uses an overlay network for the service discovery and with a built-in load balancer for scaling the services. One of the key advantages of docker swarm is that the configuration of the docker services such as volume and network can be modified without the need to manually restart the service Docker will update the configuration, stop the service tasks with the out-of-date configuration, and create new ones matching the desired configuration.
What is Docker and Docker Container ?
Docker is an open-source container platform that helps in packing an application with all its dependencies in on one bundle i.e., Docker Image. On using this docker image assigning the resources such as RAM, CPU executing it as process known as Docker Container. Docker platform make the application containerized and portable to the all systems that supports docker.
What is Docker Swarm ?
Docker Swarm is a native clustering and orchestrating tool that helps in managing the docker engines. In this the group of docker engines turned into as single virtual docker host. It facilitates the users to deploy, manage and scale the applications seamlessly across multiple docker nodes. It comes with providing the features such as service discovery, load balancing, scaling, and rolling updates. It provides an easy and integrated way to manage the containerized applications in a cluster.
What are the Task and Service in Docker Swarm ?
In Docker Swarm, a Service is a higher-level abstraction used to define how containers should be deployed, managed, and scaled across a swarm of Docker nodes. It includes specifications like the number of replicas, networking, and load balancing.
A Task is an individual instance of a container that is created and managed by a service. Each task represents a single unit of work and is scheduled to run on one of the nodes in the swarm. Tasks are the actual running containers that fulfill the requirements specified by the service.
How Does Docker Swarm Work ?
When you want to deploy a container in the swarm first, you have to launch services. Service consists of multiple containers of the same image. These services are deployed inside a node so to deploy a swarm at least one node has to be deployed. As you see below diagram the manager node is responsible for the allocation of the task, dispatch the tasks, and schedule the tasks. API in the manager is the medium between the manager node and the worker node to communicate with each other by using the HTTP protocol. The service of one cluster can be used by the other. All the execution of the task is performed by the worker node.
Docker Swarm Init
To initialize the docker swarm cluster we use the command called “docker swarm init”. For converting the docker engine to the swarm manager we will use this command after converting into the swarm mode then you will able the manager and the worker nodes then the swarm will distribute the work across them.
After Initializing The Swarm Mode
-
After initializing the docker swarm init it will bring the swarm into existence.
-
After bringing the swarm into existence know it will turn the current node into a manager node. And also it will generate one token.
-
The token that is generated will be used for the further joining of the worker nodes and master nodes.
Docker Swarm Architecture
There are two types of nodes in Docker Swarm:
-
Manager node: Carries out and oversees cluster-level duties.
-
Worker node: Receives and completes the tasks set by the manager node.
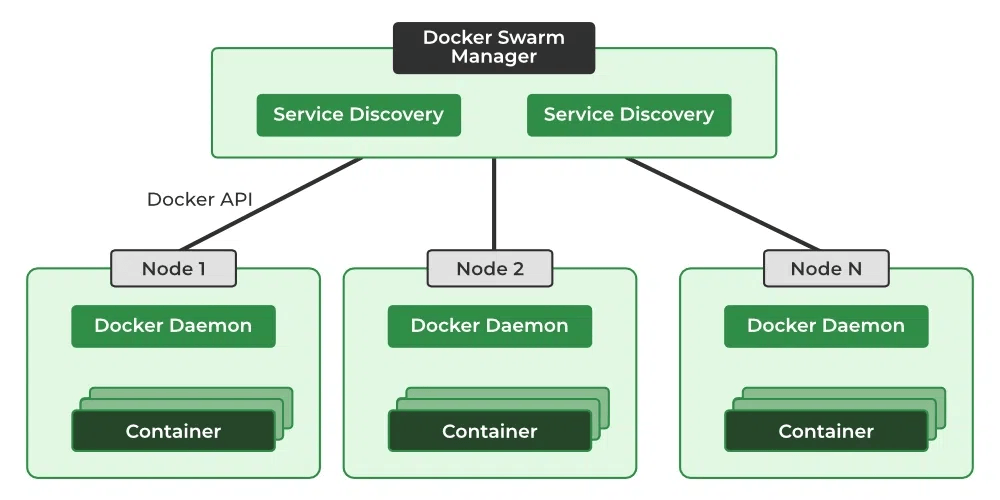
A single manager node can be created but the worker node can not be created without a manager node. The ideal number for the count of the manager node is seven. Increasing the number of the manager node does not mean that the scalability will increase.
Features of Docker Swarm
The following are the features of Docker Swarm:
-
Cluster management: To create Swarm you can use the Docker engine CLI where you can deploy the applications. Additional orchestration software is not required to manage a swarm.
-
Multi-host networking: Swarm can contain multiple overlay networks so while deploying the service you can specify the network on which you want to deploy your service. The swarm manager automatically assigns addresses to the containers on the overlay network when it initializes or updates the application.
-
Load balancing: While deploying any service on a particular port the swarm automatically balances the load of these ports.
-
Scaling: When you scale up or down, the swarm manager automatically adapts by adding or removing tasks to maintain the desired state.
What is Docker Swarm Used For ?
Docker swarm is a container orchestration tool that is used to Docker containers and scale them. Instead of a single host with the help of Docker Swarm, we can manage multiple nodes which are called clusters where we can deploy and maintain our containers in multiple hosts.
-
Docker Swarm assures that our application is always available even if one of the nodes fails by creating the container in another node which is available
-
Based on the incoming traffic we can scale the containers up and down by adding to the multiple nodes.
-
If there are multiple containers the incoming load will be balanced automatically by the Docker Swarm.
-
Docker Swarm has a number of security features, including traffic encryption between nodes and mutual TLS authentication.
-
Docker Swarm will automatically take care of failed containers and nodes. By this, we can maintain high availability.
Simply Docker Swarm is mainly used to deploy, scale, and manage the containers and nodes which are available in the cluster.
Different Modes of Docker Swarm
Docker Swarm mainly consists of two modes they are:
-
Global Mode: In this mode, Docker Swarm will maintain containers in all the slave nodes and master nodes. It will maintain the replicas of containers in all the nodes which are available in the cluster.
-
Replicated Mode: In this mode, Docker Swarm will deploy the containers based on the no.of replicas required for you. If you required 3 replicas it will deploy the containers based on the node availability.
Getting Started With Swarm Mode
Follow the steps mentioned below to get familiar with the docker swarm mode.
Step 1
In the first step we need to initialize the docker engines of swarm mode.
Step 2
After initializing the swarm mode know add the nodes into the docker swarm cluster. When you initialize the swarm mode it will generate two tokens one is for the manger node and another is for the worker node by using following command you can join the nodes according to the requirement.
docker swarm init <Token>
Step 3
Know you can start deploying the you application in the form of containers in docker swarm. Docker swarm will take care of deployment of application an scaling of the application across the worker nodes.
Step 4
With the help od docker swarm cli you can manage the swarm like adding or removing the worker nodes scaling the services and inspecting the swarm state.
What is Stack in Docker Swarm ?
A stack is nothing but a collection of one or more services deployed as a single unit. The stack is deployed by using compose file in which you can mention the service of the stack and all the required configurations to deploy the stack.
With the help of stack, it is very easy to deploy and maintain complex containers like multi-containers in the Docker swarm. We can deploy with the help of a single file called Docker Compose. yaml we can define all the necessary configurations. You can be assured that they deployed and scaled together.
If we deploy the new version of the application and the end users find any bugs while using it you can roll back to the previous version of the application by using Docker Swarm.
Note
Stack is mainly used to deploy the multi-container application with ease.
Docker Swarm Mode Key Concepts
The following are the docker swarm mode key concepts:
-
Node: A Node is an instance of a Docker engine that connects to the Swarm. You can run one or more nodes on a single physical computer or cloud server. Nodes can be either a manager or workers. The manager node dispatches units of work called tasks to worker nodes. Worker nodes receive and execute tasks dispatched from manager nodes.
-
Services: A service is a high-level concept relating to a collection of tasks to be executed by workers. An example of a service is an HTTP Server running as a Docker Container on three nodes.
-
Load Balancing: Docker includes a load balancer to process requests across all containers in the service.
Docker Swarm Filters
The following are the docker swarm filters:
-
Constraints: Based on conditions, users are restricted from creating containers on particular Docker hosts.
-
Drain Node: If we applied Drain Nodes on any node then Docker swarm will not assign any replicas to that node.
-
Port: Avoids the port conflicts between the application by deploying the same port applications in two different nodes.
Docker Swarm Mode CLI Commands
The following are the docker swarm mode CLI commands:
docker swarm init
This command is used to initialize the swarm.
docker swarm init [OPTIONS]
docker swarm join
By using this command you can join a node to a swarm. The node joins as a manager node or worker node based on the token you pass with the –token flag.
docker swarm join [OPTIONS] HOST:PORT
docker service creates
This is a cluster management command, and must be executed on a Swarm manager node.
docker service create [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
docker service inspects
This command is used to inspect the particular service and all the details will display in JSON format.
docker service inspect [OPTIONS] SERVICE [SERVICE...]
docker service ls
This command is used to see the complete list of all the services in that network.
docker service ls [OPTIONS]
docker service rm
This command is used to remove the specific service you want to remove.
docker service rm SERVICE [SERVICE...]
Docker Container vs Docker Swarm
| Aspect | Docker Container | Docker Swarm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A Docker container is an executable package that includes all code, runtime, and dependencies needed to run an app. | Docker Swarm is a container orchestration tool that manages a cluster of Docker nodes and containers. |
| Role | A container provides isolation and allows you to run an application independently. | Docker Swarm manages and orchestrates multiple containers across different nodes in a cluster. |
| OS Independence | Containers can run on any OS that supports Docker as the underlying runtime. | Swarm clusters are made up of Docker nodes that may run on different hosts and OS environments. |
| Scope | A single, isolated unit designed to run an individual application or service. | A tool for managing and coordinating multiple containers and services across a distributed network of nodes. |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for running microservices or individual applications. | Best for managing large-scale containerized applications across a cluster, offering features like scaling. |
| Functionality | Docker containers provide the necessary resources for applications to run in isolation. | Docker Swarm orchestrates the deployment, scaling, and load balancing of containers within a cluster. |
Docker Swarm vs Kubernetes
The following are the docker swarm and Kubernetes:
| Aspect | Kubernetes | Docker Swarm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Kubernetes is an open-source platform used for maintaining and deploying a group of containers. | Docker Swarm is designed to be a simple and lightweight container orchestration tool. |
| Usage with Docker | Commonly used alongside Docker for better control and management of containerized applications. | Multiple containers run efficiently on the same hardware, enhancing Docker's productivity. |
| Application Deployment | Applications are deployed as a combination of Pods, Deployments, and Services. | Applications are deployed in the form of services. |
| Auto-Scaling | Kubernetes supports auto-scaling of containers in a cluster more efficiently. | Docker Swarm supports auto-scaling but is less efficient compared to Kubernetes. |
| Health Check | Kubernetes has two types of health checks: liveness and readiness. | Health checks are limited to the service level. |
| Setup and Configuration | Kubernetes is harder to set up and configure. | Docker Swarm setup and installation are relatively easy. |
| Documentation | Kubernetes documentation covers everything from installation to deployment, though it’s less extensive compared to Docker Swarm. | Docker Swarm has more effective, extensive documentation, covering everything from installation to deployment. |
| Installation Complexity | Kubernetes installation is more difficult, with more complex commands compared to Docker Swarm. | Docker Swarm installation is simpler, requiring fewer commands for setup on virtual machines or cloud environments. |
| Adoption by Companies | Companies like Azure, Buffer, Intel, Evernote, and Shopify use Kubernetes. | Companies like Citizens Bank and MetLife use Docker Swarm. |
Docker Service vs Docker Task
The following are the differences between docker service and docker task:
| Aspect | Docker Service | Docker Task |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A higher-level abstraction that defines how to run containers as a group | An individual instance of a container created by a service |
| Purpose | Manages the deployment and scaling of a group of containers | Executes a single unit of work within a service |
| Management | Handles orchestration, load balancing, and scaling | Represents the actual work being performed by a container |
| Scalability | Easily scaled up or down to manage load | Cannot be individually scaled; scaling is done at the service level |
| State | Desired state defined (e.g., number of replicas) | Current state of a specific container instance |
| Failure Handling | Automatically reschedules tasks if a container fails | Does not manage failures; relies on the service for rescheduling |
Benefits of Docker Swarm
The following are the benefits of Docker Swarm:
-
Simplified Setup and Management: Docker Swarm provides an easy-to-use and integrated toolset for orchestrating containers, making it straightforward to set up and manage a cluster of Docker nodes.
-
Scalability: Docker Swarm allows seamless scaling of services up or down with simple commands, enabling dynamic adjustment of resources based on demand.
-
High Availability: Swarm mode ensures that services are replicated across multiple nodes, providing fault tolerance and resilience by automatically redistributing tasks in case of node failures.
-
Integrated Load Balancing: Docker Swarm includes built-in load balancing to distribute network traffic across multiple containers, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.