What is Docker ?
Docker is a set of Platforms as a service (PaaS) products that use Operating system-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Containers are isolated from one another and bundle their own software, libraries, and configuration files; they can communicate with each other through well-defined channels. All containers are run by a single operating system kernel and therefore use fewer resources than a virtual machine.
What is Docker ?
Docker is an open-source containerization platform by which you can pack your application and all its dependencies into a standardized unit called a container. Containers are light in weight which makes them portable and they are isolated from the underlying infrastructure and from each other container. You can run the docker image as a docker container in any machine where docker is installed without depending on the operating system.
Why Docker is popular ?
Docker gained its popularity due to its impact on the software development and deployment. The following are the some of the main reasons for docker becoming popular:
-
Portability: Docker facilitates the developers in packaging their applications with all dependencies into a single lightweight containers. It facilities in ensuring the consistent performance across the different computing environments.
-
Reproducibility: Through encapsulating the applications with their dependencies within a container it ensures in software setups remaining consistent across the development, testing and production environments.
-
Efficiency: Docker through its container based architecture it optimizes the resource utilization. It allows the developers to run the multiple isolated applications on a single host system.
-
Scalability: Docker’s scalability features facilitated the developers in making easier of their applications handling at time of workloads increment.
Key Components of Docker
The following are the some of the key components of Docker:
-
Docker Engine: It is a core part of docker, that handles the creation and management of containers.
-
Docker Image: It is a read-only template that is used for creating containers, containing the application code and dependencies.
-
Docker Hub: It is a cloud based repository that is used for finding and sharing the container images.
-
Dockerfile: It is a script that containing instructions to build a docker image.
-
*Docker Registry: It is a storage distribution system for docker images, where you can store the images in both public and private modes.
What is a Dockerfile ?
The Dockerfile uses DSL (Domain Specific Language) and contains instructions for generating a Docker image. Dockerfile will define the processes to quickly produce an image. While creating your application, you should create a Dockerfile in order since the Docker daemon runs all of the instructions from top to bottom.
(The Docker daemon, often referred to simply as “Docker,” is a background service that manages Docker containers on a system.)
-
It is a text document that contains necessary commands which on execution help assemble a Docker Image.
-
Docker image is created using a Dockerfile.
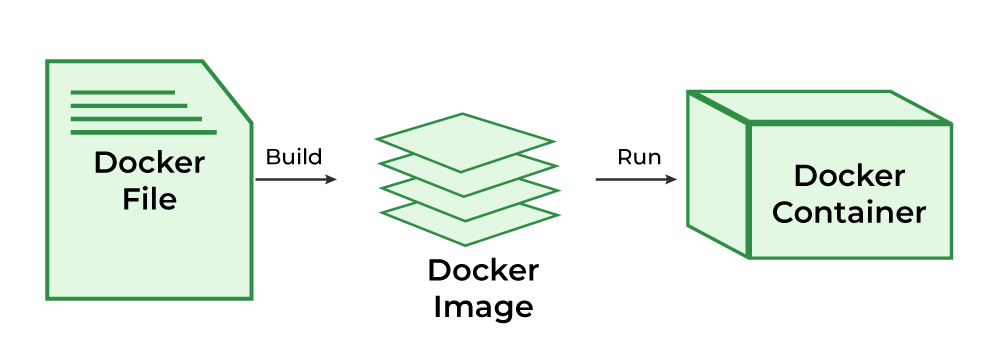
To Know more about the Dockerfile refer to the Docker – Concept of Dockerfile .
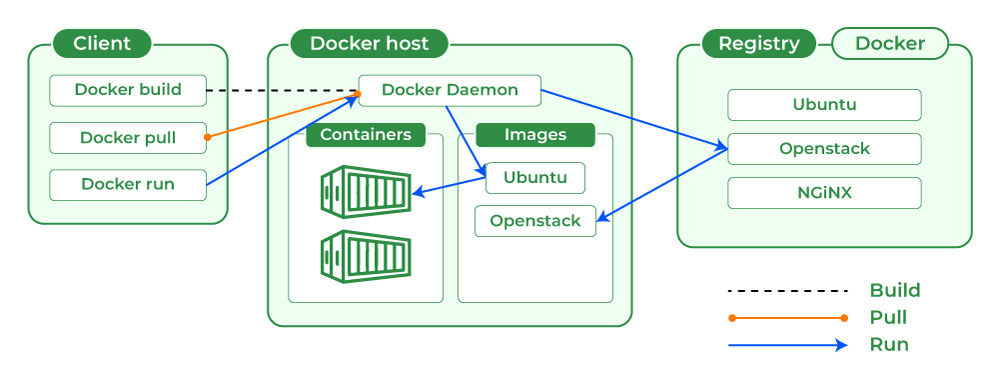
What is Docker Architecture and How Docker Works ?
Docker makes use of a client-server architecture. The Docker client talks with the docker daemon which helps in building, running, and distributing the docker containers. The Docker client runs with the daemon on the same system or we can connect the Docker client with the Docker daemon remotely. With the help of REST API over a UNIX socket or a network, the docker client and daemon interact with each other. To know more about working of docker refer to the Architecture of Docker .
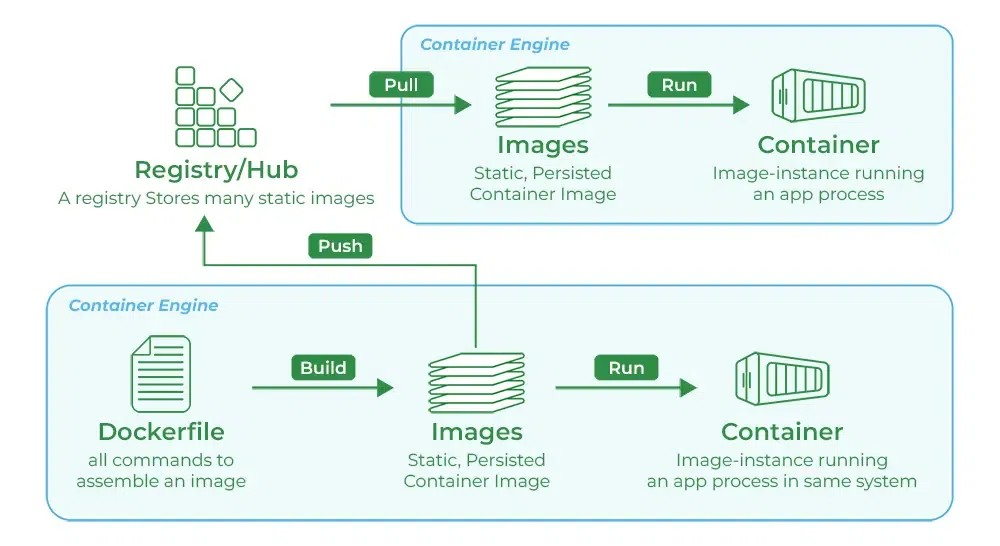
What is Docker Image ?
It is a file, comprised of multiple layers, used to execute code in a Docker container. They are a set of instructions used to create docker containers. Docker Image is an executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an application. This image informs how a container should instantiate, determining which software components will run and how. Docker Container is a virtual environment that bundles application code with all the dependencies required to run the application. The application runs quickly and reliably from one computing environment to another.
What is Docker Container ?
Docker container is a runtime instance of an image. Allows developers to package applications with all parts needed such as libraries and other dependencies. Docker Containers are runtime instances of Docker images. Containers contain the whole kit required for an application, so the application can be run in an isolated way. For eg.- Suppose there is an image of Ubuntu OS with NGINX SERVER when this image is run with the docker run command, then a container will be created and NGINX SERVER will be running on Ubuntu OS.
What is Docker Hub ?
Docker Hub is a repository service and it is a cloud-based service where people push their Docker Container Images and also pull the Docker Container Images from the Docker Hub anytime or anywhere via the internet. Generally it makes it easy to find and reuse images. It provides features such as you can push your images as private or public registry where you can store and share Docker images.
Mainly DevOps team uses the Docker Hub. It is an open-source tool and freely available for all operating systems. It is like storage where we store the images and pull the images when it is required. When a person wants to push/pull images from the Docker Hub they must have a basic knowledge of Docker. Let us discuss the requirements of the Docker tool.
What is Docker Compose ?
Docker Compose will execute a YAML-based multi-container application. The YAML file consists of all configurations needed to deploy containers Docker Compose , which is integrated with Docker Swarm , and provides directions for building and deploying containers. With Docker Compose, each container is constructed to run on a single host.
How to Download Docker Desktop ?
Docker Desktop provides GUI to work on docker containers, docker images and docker networks. Docker desktop provides and separate environment which contains Docker Engine, Docker CLI, Docker Compose, Kubernetes, and other tools which are needed to build, ship and run the applications in the form of containers which makes it more user friendly. To know more how to install docker desktop refer to Docker Desktop Sample Image.
Docker Commands
Through introducing the essential docker commands, docker became a powerful software in streamlining the container management process. It helps in ensuring a seamless development and deployment workflows. The following are the some of docker commands that are used commonly:
-
Docker Run: It used for launching the containers from images, with specifying the runtime options and commands.
-
Docker Pull: It fetches the container images from the container registry like Docker Hub to the local machine.
-
Docker ps: It helps in displaying the running containers along with their important information like container ID, image used and status.
-
Docker Stop: It helps in halting the running containers gracefully shutting down the processes within them.
-
Docker Start: It helps in restarting the stopped containers, resuming their operations from the previous state.
-
Docker Login: It helps to login in to the docker registry enabling the access to private repositories.
To Know more about the docker commands refer tot the Docker – Instruction Commands .
Docker Engine
The software that hosts the containers is named Docker Engine. Docker Engine is a client-server based application. The docker engine has 3 main components:
-
Server: It is responsible for creating and managing Docker images, containers, networks, and volumes on the Docker. It is referred to as a daemon process.
-
REST API: It specifies how the applications can interact with the Server and instructs it what to do.
-
Client: The Client is a docker command-line interface (CLI), that allows us to interact with Docker using the docker commands.
Why to use Docker ?
Docker can be used to pack the application and its dependencies which makes it lightweight and easy to ship the code faster with more reliability. Docker make its very simple to run the application in the production environment docker container can be platform independent if the docker engine is installed in the machine.
-
Resource Efficiency: Docker helps in maximizing the resource utilization by running the multiple containers on a single host. It helps in reducing the infrastructure costs and improves the efficiency.
-
Version Control: It simples the versioning for the applications and their dependencies ensuring the consistency and making easier of collaboration across the teams.
-
Microservices Agility: It enables the adoption of microservices architecture, promoting the scalability, flexibility and fault isolation agile application development.
What is Docker For AWS ?
Docker is the most powerful tool to run the application in the form of containers. Docker container are light in weight and can be run on any operating system.
AWS provides the Amazon Elastic Container Service ( Amazon ECS ) it is an fully managed container service by which you can deploy, scale and manage the docker containers. Amazon ECS is the most reliable platform according to the performance and also it can be integrated with the other AWS Service like load balancing, service discovery, and container health monitoring. To know more about Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS).
Difference Between Docker Containers and Virtual Machines
The following are the differences between docker containers and Virtual Machines:
| Feature | Docker Containers | Virtual Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Includes | Binaries, libraries, configuration files, and the application itself | A complete operating system, the application, and necessary binaries |
| Runs on | Underlying OS kernel (no guest OS per container) | Hypervisors, which allow multiple VMs to run on a single machine |
| Size & Resource Usage | Lightweight, as they don’t contain a guest OS | Larger, each VM has its own OS, requiring more resources |
| Resource Sharing | Shares resources with other containers in the same host OS | Isolated hardware resources |
| Process Isolation | OS-level process isolation | Hardware-level process isolation |
| Boot Time | Fast to boot | Slow to boot |
Importance of Docker
The following are the some of the insights that discusses on the importance of docker:
-
Efficiency and Speed: It facilitates with providing the streamlined development and deployment by packaging applications with dependencies into consistent containers.
-
Resource Optimization: It helps in sharing host system resources efficiently, allowing for higher application density and cost savings.
-
Scalability and Portability: It is easily able to scale the applications and ensures seamless movement across different environments.
-
Isolation and Security: it provides high isolation, reducing conflicts and enhancing security.
Benefits of Docker
The following are the some of the benefits of Docker:
-
Portability: Docker facilities with creation of lightweight portable containers that can be unable on any machine regardless of the underlying operating systems.
-
Isolation: Docker through containers provides a high level of isolation with enabling the applications to run independently of each other addressing the issues that one container doesn’t impact on other.
-
Reproducibility: With, Docker developers can easily package their applications and their dependencies into a reusable images. It allows for consistent and repoduciable builds across the development, testing and production environments.
-
DevOps Integration: It promotes the collaboration and automation across the software development life cycle in handing the increasing workloads.
Alternatives of Docker
The following are the alternatives of Docker:
-
Podman: Offers a Docker-compatible container engine with a focus on security and compatibility, ideal for environments where Docker is not preferred or available.
-
rkt: A lightweight container runtime developed by CoreOS, designed for simplicity, security, and composability, offering an alternative to Docker’s container runtime.
-
LXC (Linux Containers): Provides operating-system-level virtualization for running multiple isolated Linux systems (containers) on a single host, offering a lightweight alternative to Docker for certain use cases.
-
containerd: An industry-standard core container runtime developed by Docker, Inc., offering a minimal and stable platform for building containerized applications, often used as a lower-level alternative to Docker for more advanced container orchestration systems like Kubernetes.
Docker Security
The following are the some of the insights on docker security:
-
Isolation: Docker containers provides the strong isolation ensuring the applications and processing its running.
-
Immutable Infrastructure: It promotes the use of immutable infrastructure, where containers are build from the immutable images that are version controlled.
-
Resource Constraints: It allows you to define the resource constraints for containers such as CPU and memory limits.
-
Security Scanning: It provides the built-in security scanning tools that allows you to scan the container images for known vulnerabilities and malware before deployment.
Use Cases of Docker
The following are the some of the use cases of Docker:
-
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): It helps in streamlining and automating the software delivery process with ensuring faster and more reliable releases.
-
Microservices Architecture: It facilitates the development, deployment, and management of microservices with enabling independent scaling and maintenance.
-
Development Environment Consistency: It will ensures with consistent development, testing, and production environments, reducing “it works on my machine” issues.
-
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Deployments: It helps in simplifying the application deployment across various cloud platforms, enhancing flexibility and reducing vendor lock-in.
Best Practices and Tips for using Docker Effectively
The following are the best practices and tips of using docker effectively:
-
Use Official Images: Try to always start with official images from Docker Hub to ensure security and reliability.
-
Minimize Image Size: Keep your Docker images as small as possible by using multi-stage builds and removing unnecessary files.
-
Leverage Docker Compose: Use Docker Compose for managing multi-container applications, simplifying setup and deployment.
-
Implement Proper Security Measures: Regularly update images, avoid running containers as root, and use network segmentation to enhance security.
Docker Vs Kubernetes
The following are the difference between docker and kubernetes:
| Feature | Docker | Kubernetes |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Containerization platform | Container orchestration platform |
| Functionality | Creates and manages containers | Manages and scales containerized applications |
| Setup Complexity | Simple to set up and use | More complex setup and configuration |
| Scalability | Limited to single-node scaling | Designed for large-scale, multi-node environments |
| Networking | Basic networking capabilities | Advanced networking with service discovery and load balancing |
| State Management | Stateless; manages individual containers | Stateful; manages container clusters and services |
| Use Case | Development and testing environments | Production environments with high scalability and reliability requirements |
To known more the difference between docker and kubernetes, refer this – Article
Conclusion
So you have learned about the basics of Docker, the difference between Virtual Machines and Docker Containers along some common terminologies in Docker. Also, we went through the installation of Docker on our systems. We created an application using Docker and pushed our image to Docker Hub. Lastly, we learned how we could remove a particular image from our local system and later pull the image from Docker Hub if it doesn’t exist locally.