How to Run a Python Script using Docker ?
Docker helps you to run your python application very smoothly in different environments without worrying about underlying platforms. Once you build an image using dockerfile you can run that image where ever you want to run. Docker image will help you to package all the dependencies required for the application which will used for further while running the container.
What is Docker ?
Docker is a set of platforms as a service (PaaS) products that use the Operating system level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Containers are isolated from one another and bundle their own software, libraries, and configuration files; they can communicate with each other through well-defined channels. All containers are run by a single operating system kernel and therefore use fewer resources than a virtual machine. To know more about docker refer to Introduction to Docker.
Key Terminologies
Docker mainly depends on the following three components as mentioned below.:
-
Dockerfile: Dockerfile is a source code of a docker image. It consists of set instructions to build a docker image.
-
Image: The instructions which are given in the dockerfile are called layers in the docker image. Docker image consists of several layers according to the no. Of instructions, you have given.
-
Container: Docker image helps to build docker containers which are lightweight and easy to portable from one platform to another platform. Docker container is a running instance of docker image.
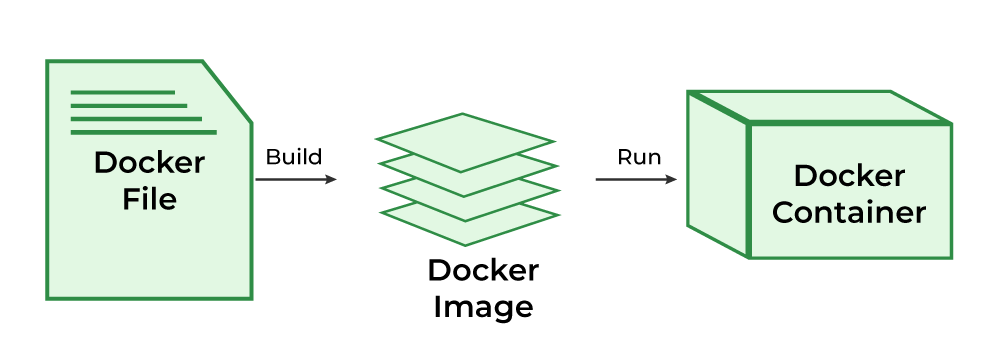
Dockerfile Instruction
There is a Docker syntax that you need to follow while writing the dockerfile as shown below:
INSTRUCTION arguments
Most frequently used instructions in dockerfile are as follows:
-
FROM
-
RUN
-
ADD
-
ENV
-
ENTRYPOINT
-
CMD
This is some of the instructions which are regularly used in dockerfile to know more about the syntax of dockerfile refer to What is Dockerfile Syntax?.
Docker Commands
Docker commands make your work easier which will help you to manage the docker containers like removing containers, running docker image as a container,and managing the containers and so on some of the most commonly used docker commands are.
-
docker run
-
docker ps
-
docker stop
-
docker rm
-
docker images
-
docker pull
To know more about docker commands refer to the Docker – Instruction Commands.
Installing Docker
To run docker container first you need to install docker in your local machine you can install docker in different operating systems
-
For Windows: How to Install Docker on Windows?
-
For macOS: How to Install Docker on macOS?
-
For Linux/UNIX: How To Install and Configure Docker in Ubuntu?
Creating Dockerfile For Python Application
Running Python scripts in a Docker container is an efficient way to ensure consistency across environments. If you’re looking to expand your knowledge of containerization and how Docker fits into the full DevOps lifecycle, the DevOps Engineering – Planning to Production course offers a comprehensive guide to containerization and Docker best practices.
Here are the detailed steps to create dockerfile for python application:
Step 1: Creating the Files and Folders
We will be creating a Folder docker_2 at the desktop location in our PC . Inside the Folder another Folder called docker_assignment is created. Then two files dockerfile and test.py are created in this folder.
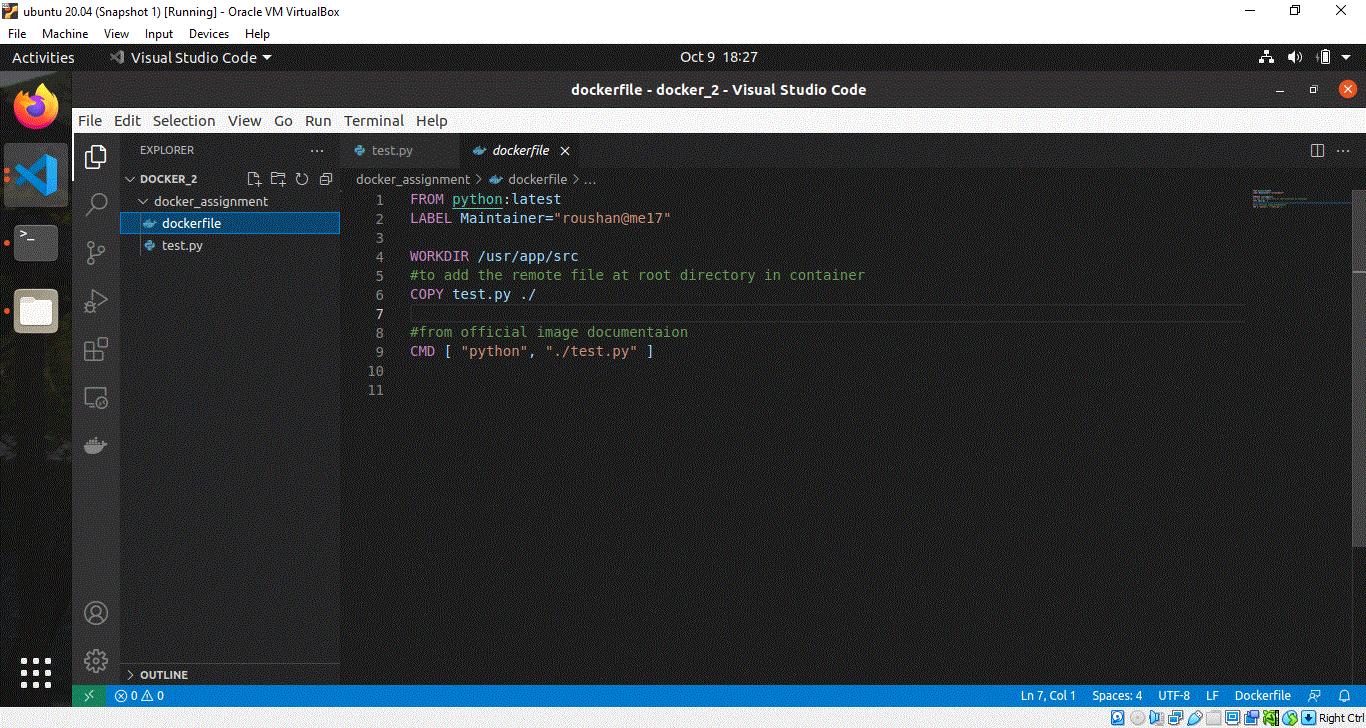
Step 2: Creating the Dockerfile
Inside the dockerfile we will start by first taking the python base image from docker hub. A tag latest is used to get the latest official python image. It is very important to set your working directory inside your container. I have chosen /usr/src/app. All commands will be executed here as well as the images will be copied here only.
I have then copied the test.py file from my pc to the container current working directory(./ or /usr/src/app) by using the COPY command.
#Deriving the latest base image
FROM python:latest
#Labels as key value pair
LABEL Maintainer="roushan.me17"
# Any working directory can be chosen as per choice like '/' or '/home' etc
# i have chosen /usr/app/src
WORKDIR /usr/app/src
#to COPY the remote file at working directory in container
COPY test.py ./
# Now the structure looks like this '/usr/app/src/test.py'
#CMD instruction should be used to run the software
#contained by your image, along with any arguments.
CMD [ "python", "./test.py"]
Build The Docker Image For Python Application
Step 1: Building the Docker Container
After you have created both the Python script and the Dockerfile, you can now use the Docker build command to build your Docker Image.
Here -t is for adding tags to identify your image easily.
docker image build -t python:0.0.1 /home/roushan/Desktop/docker_2/docker_assignment
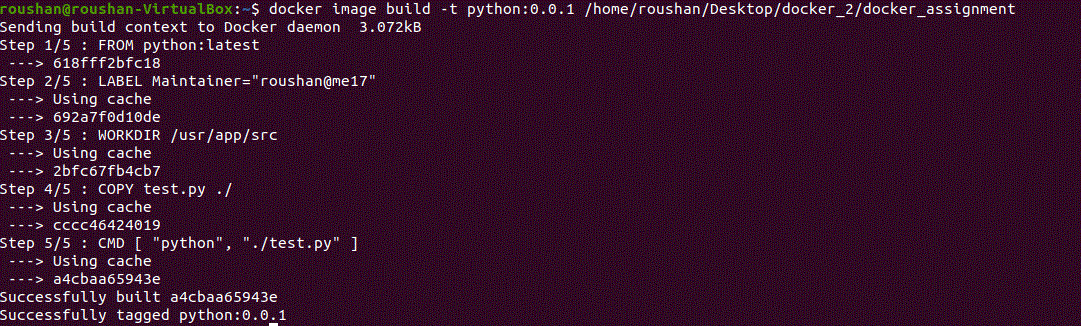
Step 2: Verify the Image Build
After you have built your Docker Image, you can list all the Images to check whether your image has been successfully built or not.
docker images
You will find your Image name listed here and with the tag name, you can easily find it.

Run The Docker Container For Python Docker Image
Now, you can use the Docker run command to run your Docker Container.
docker run python:0.0.1
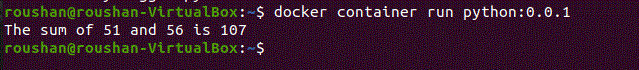
After running the Docker Container, you will see the output printed after adding the two numbers.
Conclusion
To conclude, in this article, we saw how to build a simple addition Python script and run it inside the Docker Container.