Kubernetes – Kubectl Commands
The Kubernetes command-line tool, kubectl, allows you to run commands against Kubernetes clusters. You can use kubectl to deploy applications, inspect and manage cluster resources, and view logs. Some basic Kubectl commands in a Kubernetes cluster are as follows:
kubectl Commands
The most popular kubectl commands and flags are listed below.
1. Common Commands
| Name | Commands |
|---|---|
| Run a two-replica nginx deployment | kubectl run my-nginx --image=nginx --replicas=5 --port=80 |
| Run and expose the Nginx pod | kubectl run my-nginx --restart=Never --image=nginx --port=80 --expose |
| Run nginx deployment and expose it | kubectl run my-nginx --image=nginx --port=80 --expose |
| List of nodes and pods | kubectl get pod -o wide |
| List all of them | kubectl get all --all-namespaces |
| Get every service | kubectl get service --all-namespaces |
| Show labeled nodes | kubectl get nodes --show-labels |
| Using a dry run, verify the yaml file | kubectl create --dry-run --validate -f pod-GFG.yaml |
2. Check Performance
| Name | Command |
|---|---|
| Learn about node resource use | kubectl top node |
| Obtain pod resource use | kubectl top pod |
| Get the resource utilization for the specified pod | kubectl top <podname> --containers |
| List each container’s resource usage | kubectl top pod --all-namespaces --containers=true |
For deeper hands-on experience with Kubernetes and mastering Kubectl commands, the DevOps Live Course provides comprehensive training on Kubernetes, Docker, and other essential tools in DevOps environments.
3. Label & Annotation
| Name | Commands |
|---|---|
| By label, sort the pods | kubectl get pods -l owner=gfg |
| Add a label by hand to a pod | kubectl label pods <podname> owner=gfg |
| Remove label | kubectl label pods <podname> owner- |
4. Secrets
| Name | Commands |
|---|---|
| List secrets | kubectl get secrets --all-namespaces |
| Obtain a certain hidden field of secret | kubectl get secret GFG-cluster-kubeconfig |
5. Service
| Name | Commands |
|---|---|
| List all services | kubectl get services |
| List service endpoints | kubectl get endpoints |
| Get service detail | kubectl get service <servicename> -o yaml |
6. Volumes & Volume Claims
| Name | Commands |
|---|---|
| List storage class | kubectl get storageclass |
| Check the mounted volumes | kubectl exec storage<nameofpv> |
| Check persistent volume | kubectl describe <nameofpv> |
Kubectl apply
We can update or apply the configuration to a cluster with the aid of “kubectl apply”. With the help of the apply command, Kubernetes resources can be modified and created using a configuration file or a collection of configurations from a directory.
Creating objects: The basic syntax of “kubectl apply”
kubectl apply -f <filename.yaml>
Viewing and Finding Resources
These commands are used to show all the resources. It works like a READ operation. It is used to view resources like nodes, deployments, services, config maps, etc.
kubectl get <resource>
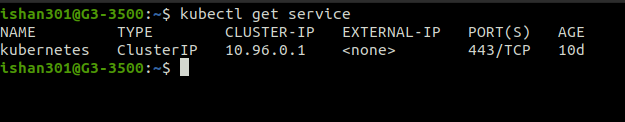
Getting all Resources
The “kubectl get all” command enables us to view all the cluster’s resource
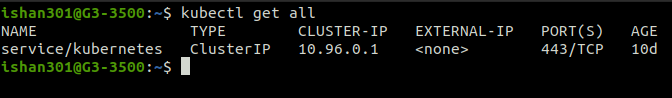
Getting Nodes
The number of available nodes in the cluster will be displayed by “Kubectl get nodes”.
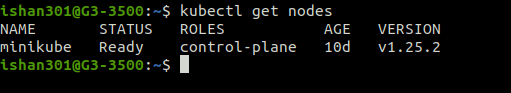
Getting Pods
“Kubectl get pod” can be used to find out how many pods are scheduled in the cluster.
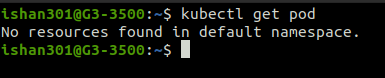
Getting Services
“Kubectl get service” can be used to list the services that have been created in the cluster.
Creating Resources
These commands are used to create resources like deployments, services, secrets, config maps, etc.
kubectl create <resource_type> <resource_name> OPTIONS
Creating Deployment
The command creates a deployment named nginx-depl using the image Nginx.
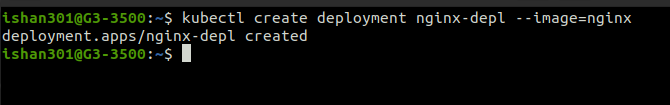
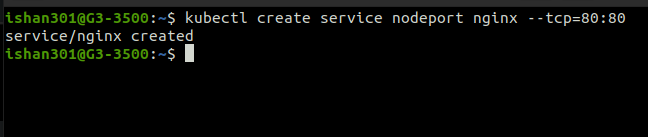
Creating service
The command in the creates a service of type node port named nginx, and it is exposed on port 80 of the local machine
Editing Resources
After running the command below you can update the resource configuration file and if there are any changes the resource will be updated according to it.
kubectl edit <resource_type> <resource_name>
Updating Deployment
The command in the below output opens a Vim-like editor in the terminal to edit the Nginx-deal deployment config file.
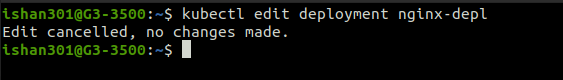
Updating Service
The command opens a vim-like editor in the terminal to edit the Nginx service config file.
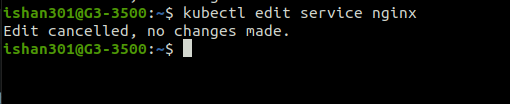
Deleting Resources
These commands are used to delete resources like deployments, services, config maps, pods, secrets, etc. You can choose a particular resource name of a resource type or you can also delete all resources of a resource type by specifying –all flag
kubectl delete <resource_type> <resource_name> | --all
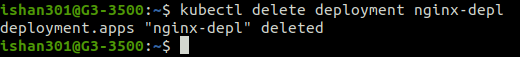
Deleting Deployment
The command deletes a deployment named nginx-depl.
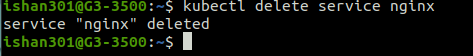
Deleting Service
The command deletes a service named Nginx.
Using Configuration File for CRUD
These commands are used to use YAML configuration files for CRUD operations in a cluster.
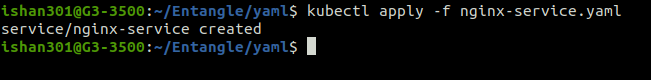
Applying a Config file
The command creates the resource if it does not exist or updates it if it already exists according to the configuration in the YAML file mentioned after the -f flag.
kubectl apply -f [file-name]
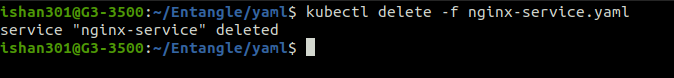
Deleting using Config file
The command deletes the resource that was created using the YAML config file mentioned after the -f flag
Interacting with running Pods
Viewing Logs of a Pod
The command shows the logs of the pod mentioned once the pod started.
kubectl logs [pod-name]
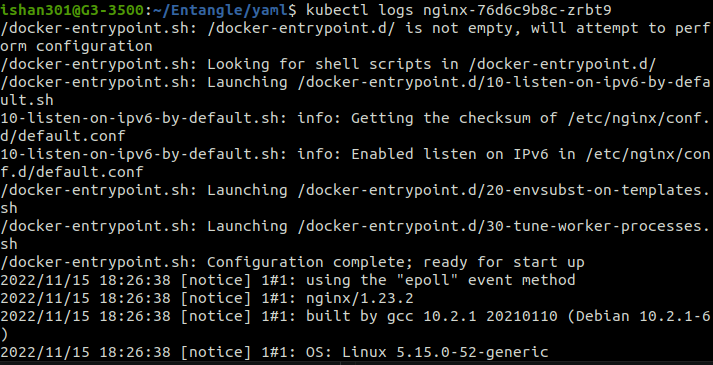
Get an Interactive terminal for a pod
The command starts an interactive terminal of the Nginx pod so that we can control the pod directly through its terminal.
kubectl exec -it [pod-name] -- bin/bash

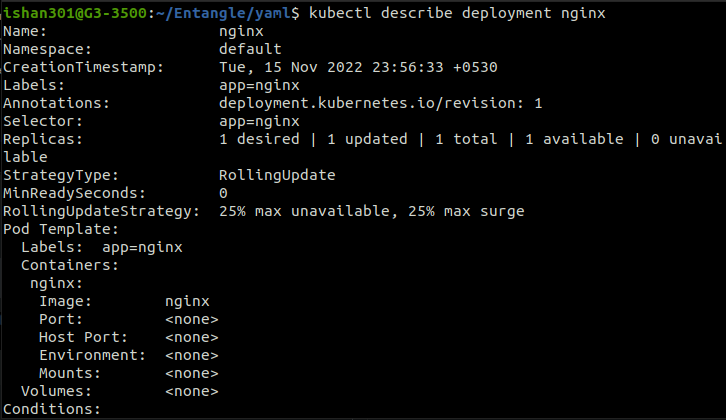
Get info about a Resource
The command gives details about the nginx deployment.
kubectl describe <resource_type> [resource-name]
Copying Files and Directories to and from Containers
With the help of the “kubectl cp” command, we can copy files from host to container and vice versa.
The basic syntax of “kubectl cp”
kubectl cp <host path pod name:container path>
This command will only function if the “tar” command in the container images is present or the command failed to run.
Updating Resources
The “kubectl get rs” command allows us to check the list of deployments, To update them, look up the revision history of prior deployments, and roll back to a specific revision if necessary. Using the following commands.
kubectl rollout <history> , <undo> , <status>, <restart>