Kubernetes – Creating Multiple Container in a Pod
Kubernetes is a container management tool, and it automates container deployment, load balancing, and container scaling. It is open-source and developed by Google in 2014 and written in Golang. All cloud providers adopt Kubernetes. It is scheduled runs and manages isolated containers that are running on virtual, physical, and cloud machine
-
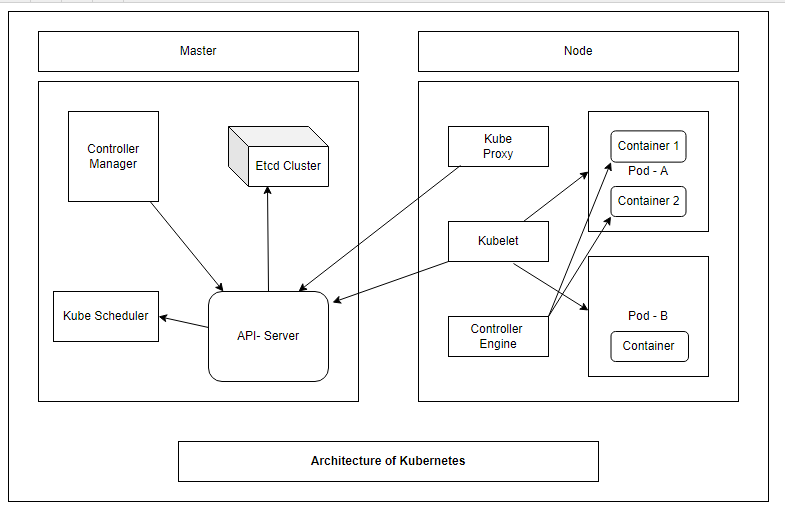
Kube API-Server – API–Server directly interacts with the user as per instruction written in the YAML file or JSON file, and it is the front-end of the control plane
-
ETCD – It is a Consistent, highly available store and open-source distributed system. It stores the status of the cluster and metadata of all configurations as well as manages the critical data. The key feature of etcd:
- Secure
- Fully replicated
- Fast
- High Available
-
Controller Manager – The controller manager makes sure that the actual states of the cluster match to desired states
-
Kube–Scheduler – When the users make requests for the Creation and Management of pods, Kube-scheduler is going to take action on these requests. Kube-scheduler assigns any node to create and run pods
-
Pod – A pod is like a group of one or more containers deployed together on the same pod. IP address assignment with the pod, not the container that’s why the good practice is to create one container in one pod. If a person has required then create multiple containers in the same pod.
-
Container – A running stage of the image with all required dependencies or software is called a container. It is lightweight and deployed within a minute. It does not require pre-allocation of RAM.
-
Kube-Proxy – Kube-Proxy assigns the unique IP address to each pod. In Kubernetes, the pod gets the address, not the container that’s why it is a good practice to create one container in one pod.
-
Kubelet – Kubelet is running in the node, and it is an agent. It manages and deployment the pods and nodes interact with the master with the help of Kubelet. It receives the instruction from the API server.
Create Multiple Containers in a Pod
Step 1
Open your machine with successfully installed Kubernetes
Step 2
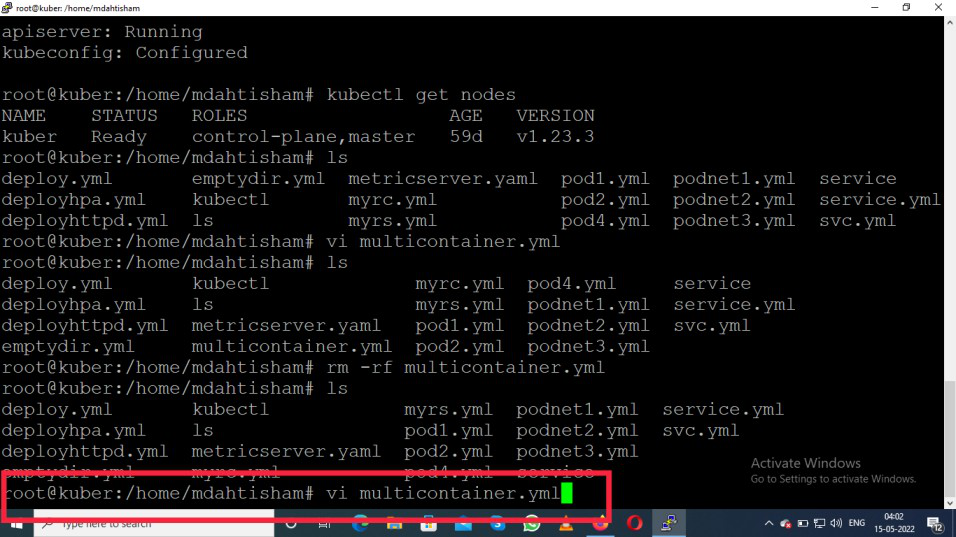
First of all, create a Manifest file. If a person wants to do anything in Kubernetes first required to create a Manifest. Manifest is a file using the YAML(Yet Another Markup Language)
vi multicontainer.yml
-
Press enter button then the editor will open
-
Then press the “i” button to type the YAML code in the editor
YAML Code for Creating Multiple Containers in a Pod:
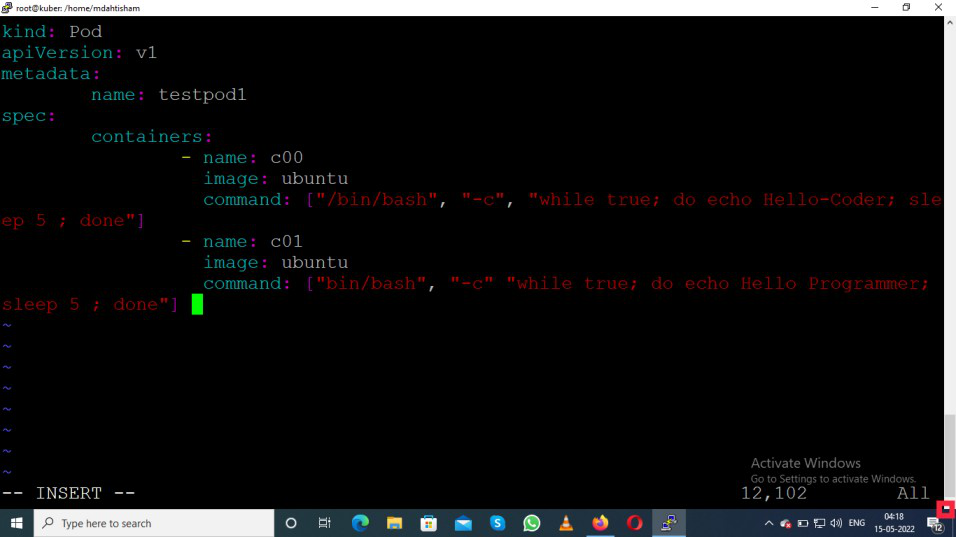
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: testpod1
spec:
containers:
- name: c00
image: ubuntu
command: ["/bin/bash", "-c", "while true; do echo Hello-Coder; sleep 5 ; done"]
- name : c01
image: ubuntu
command: ["/bin/bash', "-c" , "while true; do echo Hello-Programmer; sleep 5 ; done"]
-
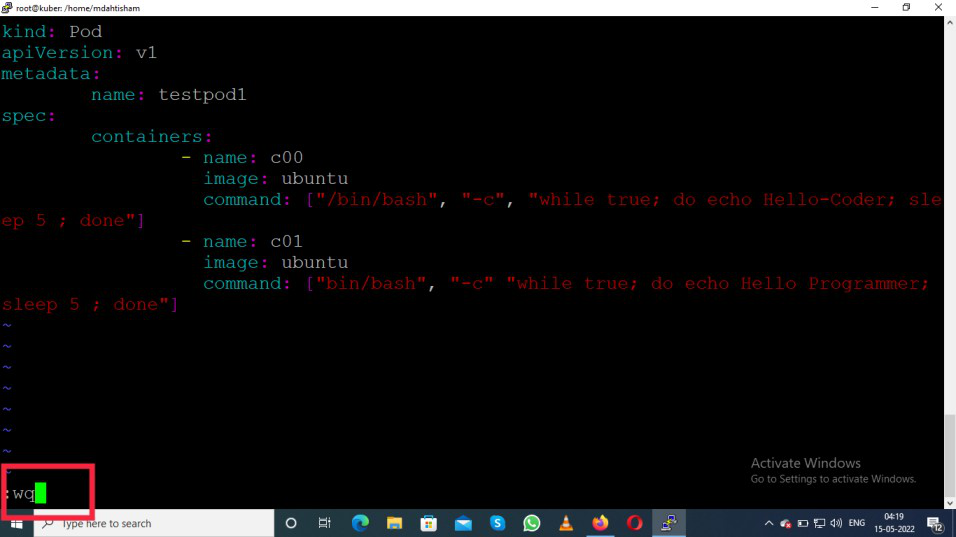
Press the "ESC" button
-
Then press the ":wq" to save the code and exit the editor
Step 3
Execute the file with the help of the command.
kubectl apply -f multicontainer.yml
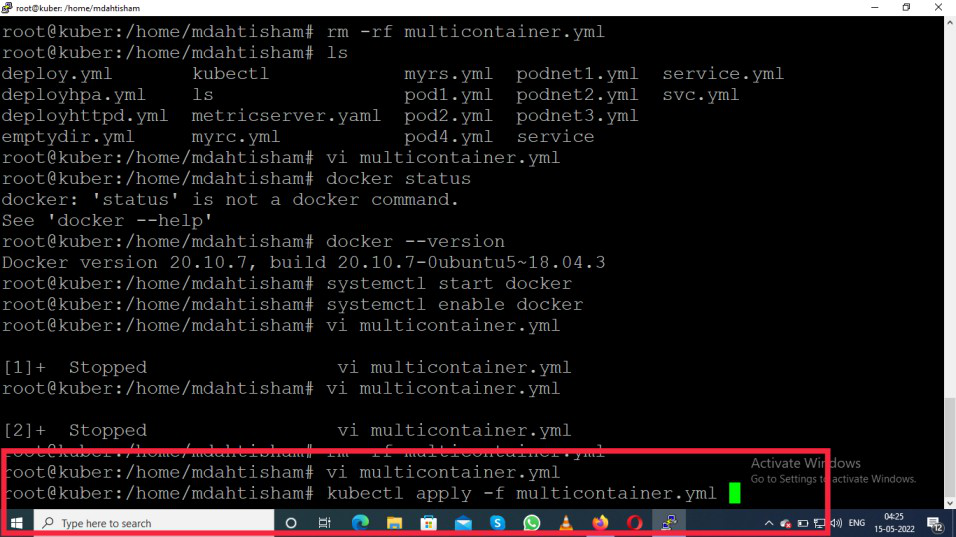
Then it will show testpod1 created.
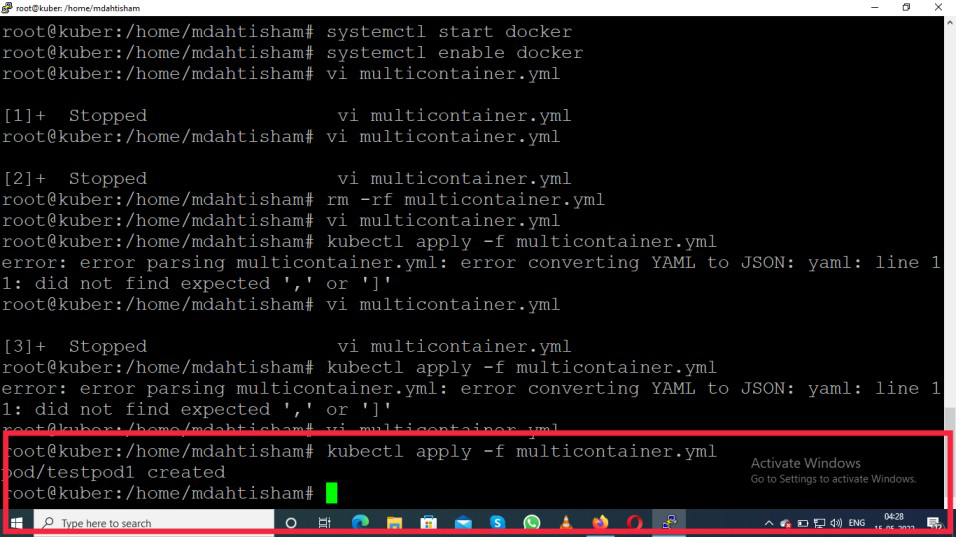
Step 4
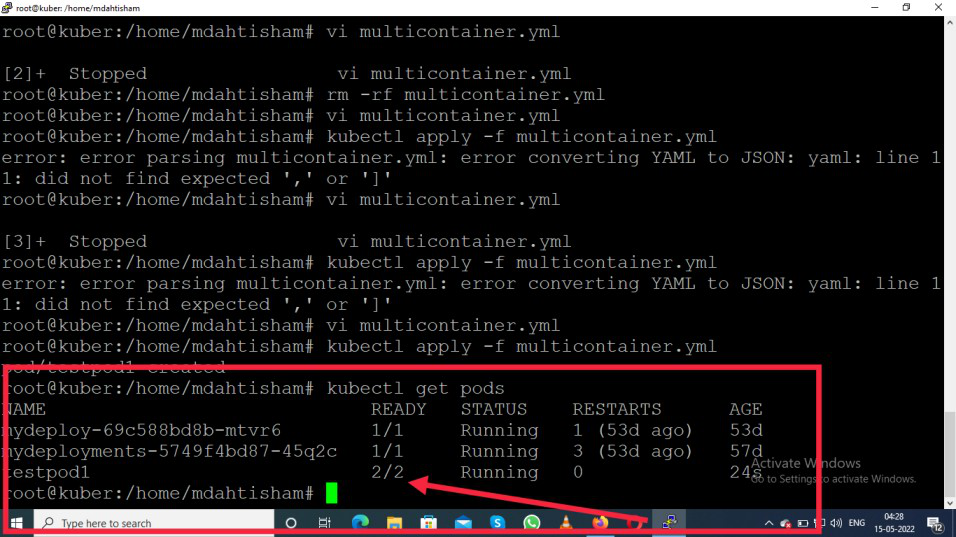
Check whether your pod is ready or not
kubectl get pod
Output:Name - testpod1 , Ready- 2/2, Status - Running
It means the pod is ready with two container
-
If a person wants to check both container one by one then used this command
-
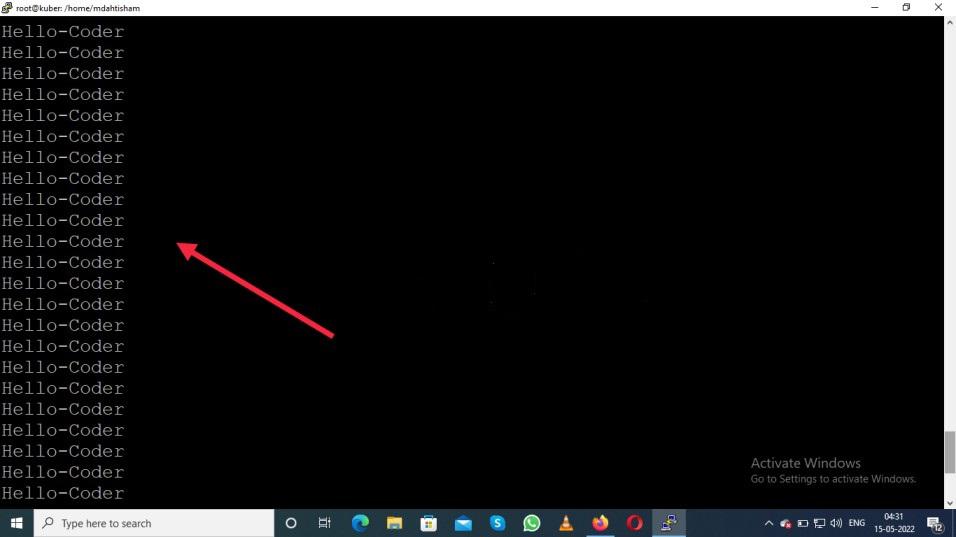
First container c00
kubectl logs -f testpod1 -c c00
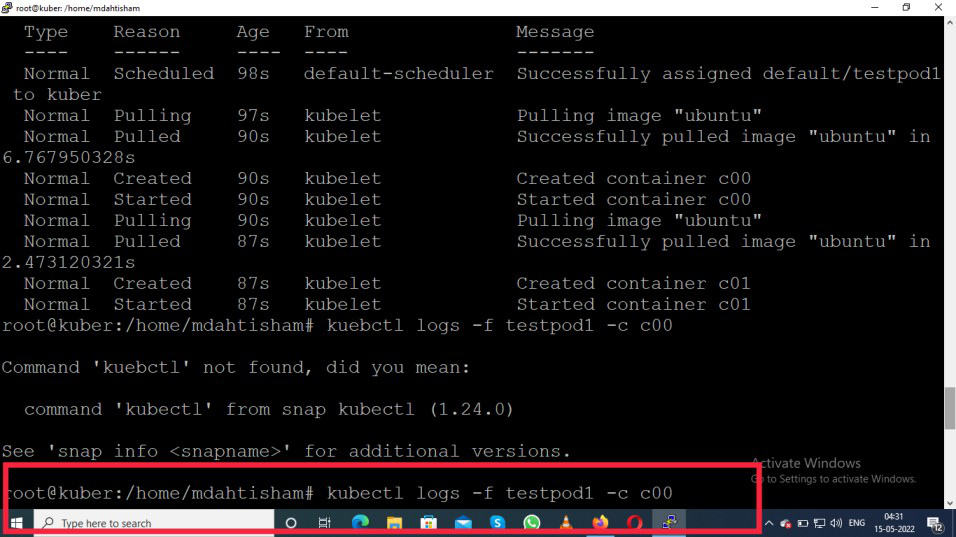
Output
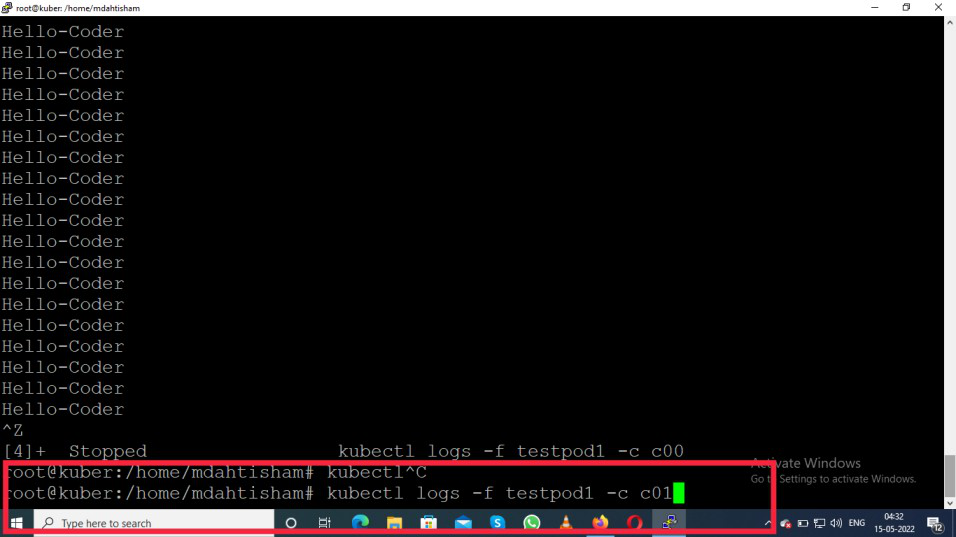
- Check second container c01
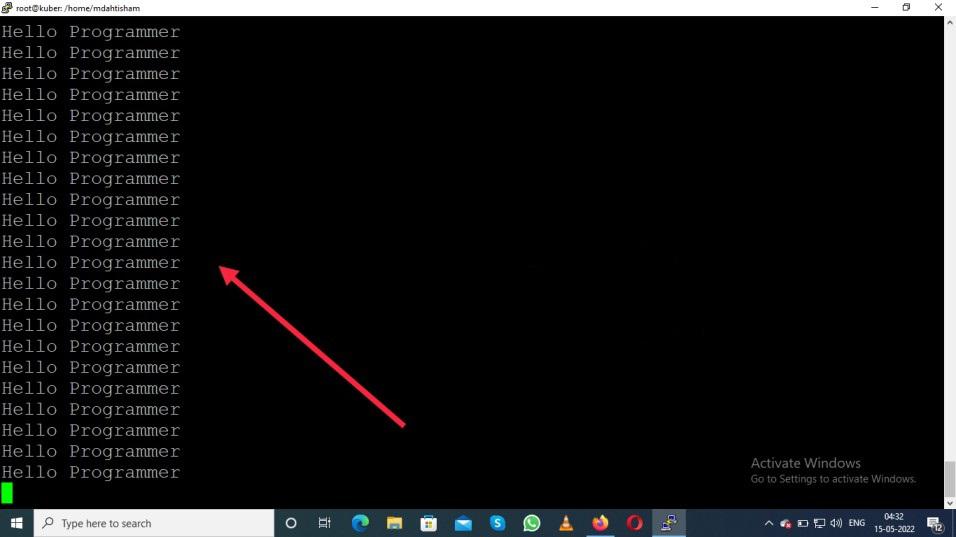
kubectl logs -f testpod1 -c c01
Output
Note
Pod name - testpod1
1st Container name - c00
2nd Container name - c01