Kubernetes – NodePort Service
NodePort service in Kubernetes is a service that is used to expose the application to the internet from where the end-users can access it. If you create a NodePort Service Kubernetes will assign the port within the range of (30000-32767). The application can be accessed by end-users using the node’s IP address.
Kubernetes Service
Kubernetes service will help you to expose the pods that are running in the cluster to the outside world, and also they will make it available for the pods to each other that are running in the Kubernetes cluster.
Types Of Kubernetes Services
In Kubernetes, there are 3 types of services to provide discovery and routing between pods.
-
ClusterIP: It is the default service and its visibility is cluster internal which means it’s not possible to use clusterIP service to reach a microservice from the internet from outside the cluster.
-
NodePort: NodePort extends the ClusterIP service and its visibility is internal and external to the cluster. You can set a NodePort using the NodePort property, this is the port that the service will listen on from outside the cluster. There is one requirement of using NodePort which is nodes must have public IP addresses. The port must be in the range between 30000 and 32767 and if you don’t specify the NodePort value Kubernetes will assign it randomly.
-
LoadBalancer: It operates at the transport level (TCP) that is at level 4. It means that is unable to make decisions based on content, and it uses a simple algorithm such as a round-robin across the selected paths. Whereas Ingress operates at the application level which is at level 7. It is able to make decisions based on the actual content of each message. More intelligent load-balancing decisions and content optimizations. In other words, Ingress is like a LoadBalancer but more intelligent.
For our article, we’ll use NodePort service for service discovery.
Kubernetes NodePort Service
Kubernetes NodePort Service is a service which is used for to expose the nodes which are available in the cluster to the outside of the cluster. It will also expose the applications which are running in the node it also allows the traffic from the outside to reach the application with the help of NodePort. To learn how to manage NodePort services and other Kubernetes components within a DevOps workflow, the DevOps Engineering – Planning to Production course provides practical examples of Kubernetes networking.
Example Of NodePort Service
Following is the sample YAML file for the kubernetes NodePort Service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: <Name Of the Service>
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80 # Port exposed within the cluster
targetPort: 8080 # Port on the pods
nodePort: 30000 # Port accessible externally on each node
selector:
app: example-app # Select pods with this label
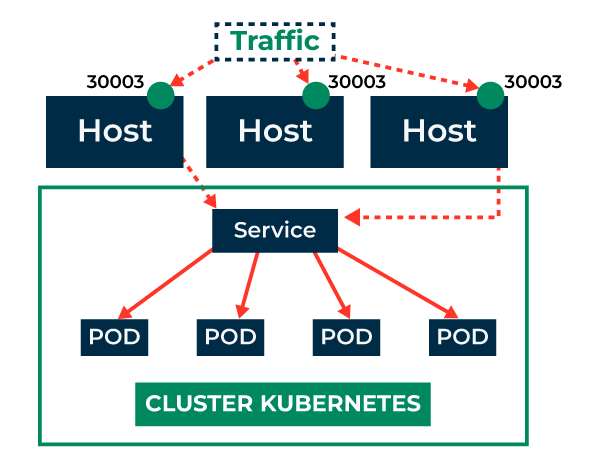
How NodePort Service Work ?
NodePort service will expose the pods of node to the another, and also it will expose the pods to the outside of the cluster from where the users can access from the internet by using the IP address of node and port.
Following is the sample YAML file for NodePort Service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
selector:
app: my-app
type: NodePort
ports:
– protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
APIVersion of the service is V1 and the kind was service there are two important things to consider here first one is above YAML file you can see port 80 and targetPort 80 the major difference between this two was Port on which port does service expose the pod outside and the target port is the port where pod listens.
Steps To Use NodePort Service
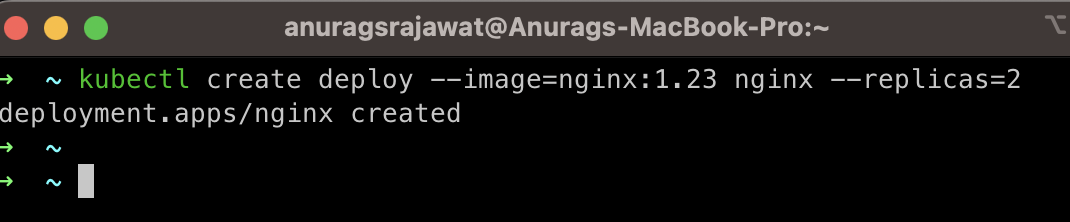
Step 1
Create a deployment. For our demo purpose, I choose Nginx as our application with 2 replicas, you can change it as per your requirement.
kubectl create deploy --image=nginx:1.23 nginx --replicas=2
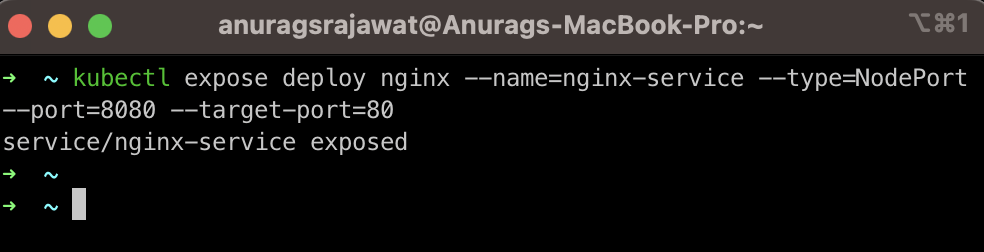
Step 2
Expose service with NodePort
kubectl expose deploy nginx --type=NodePort --port=8080 -target-port=80
we exposed our deployment as a NodePort service with the name nginx-service
Check your service (Optional):
kubectl get svc nginx -service -o wide
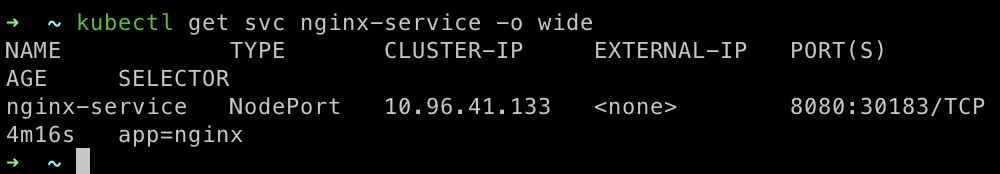
You can see we’ve successfully exposed our service with NodePort
Step 3
Access your application
minikube service nginx-service --url
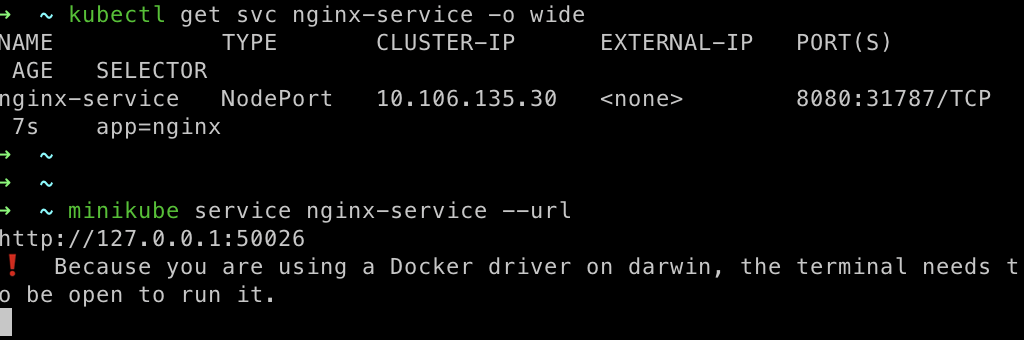
On invoking this, you can see it in the browser:
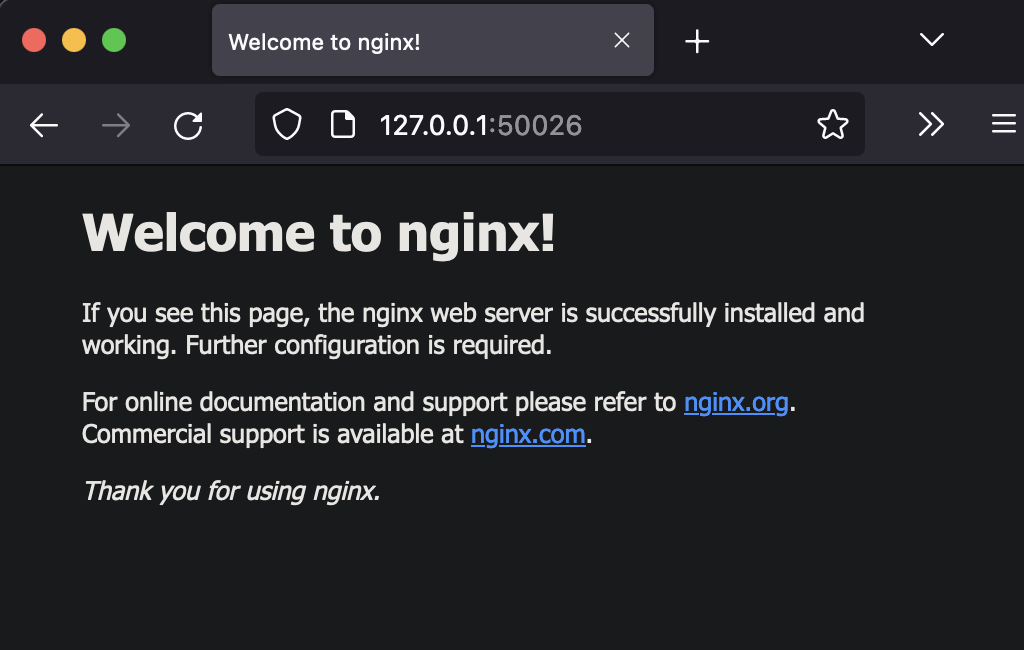
As you can see in the above image we can access our application on our machine which is running on our cluster, this is only possible because of the NodePort service.
Difference Between NodePort And ClusterIP
| Aspect | NodePort | ClusterIP |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exposes the service on a static port across each node's IP, allowing external traffic to reach the pod | Exposes the service on an internal IP, only accessible within the cluster |
| Purpose | Used when you want to expose the pods externally and also internally within the cluster | Used for internal communication within the cluster, not accessible externally |
| Use Case | Suitable for exposing applications like web applications that need to be accessed from outside the cluster | Ideal for internal services like databases or internal APIs that don’t require external access |
| Traffic | Allows external traffic from the internet to access the service | Restricts access to internal traffic within the Kubernetes cluster |
| Scenario | If you want a service accessible both externally and internally, use NodePort | If you want a service only for internal use, such as internal APIs or databases, use ClusterIP |
NodePort service is used to expose the application outside of the cluster and ClusterIP is used to access for internal purpose only.