Kubernetes – How to Run Shell Commands in Kubernetes Pods or Containers
In Kubernetes, we create pods by adding an extra layer of information on containers. This Kubernetes in short is known as K8s, an open-source container orchestration tool developed by Google. It is used to orchestrate the containers for bringing Agility in software deployment through scaling, and management. Currently, it is being maintained by the cloud native computing foundation (CNCF).
Kubernetes Cluster Setup
Firstly ensure setting up the Kubernetes cluster, It can be done either Through an Original Setup with multiple nodes or with a simple single-node Kubernetes cluster setup using software such as Minikube. The major difference between Kubernetes and Minikube is that on Minikube you only have a single node instead of a node cluster. Due to this, we do not have to go through the trouble of setting up the entire Kubernetes configuration. To know more about Setting Up Minikube in Your Local System Read this – Article.
Understanding Of Kubernetes Pods And Containers
Kubernetes pods are the smallest deployable units in the Kubernetes cluster. A pod comes representing one or more containers with tight bonding and sharing the same network namespace and storage. You can think as pods the extra layers on top of the containers with metadata information provide effective orchestration with tools like Kubernetes. These pods encapsulate the application’s code, runtime, libraries, and dependencies bringing consistency across diverse environments.
Now let us see the working of commands inside a K8s pod. A pod in K8s is a single instance of an application, and it is the smallest entity inside K8s.
Execute Commands Inside The Kubernetes Pod
Here, we are using Minikube setup Kubernetes cluster. Firstly Download the software as per your supporting System Configurations and then follow the below steps to execute the commands inside the Kubernetes Pod.
Step 1
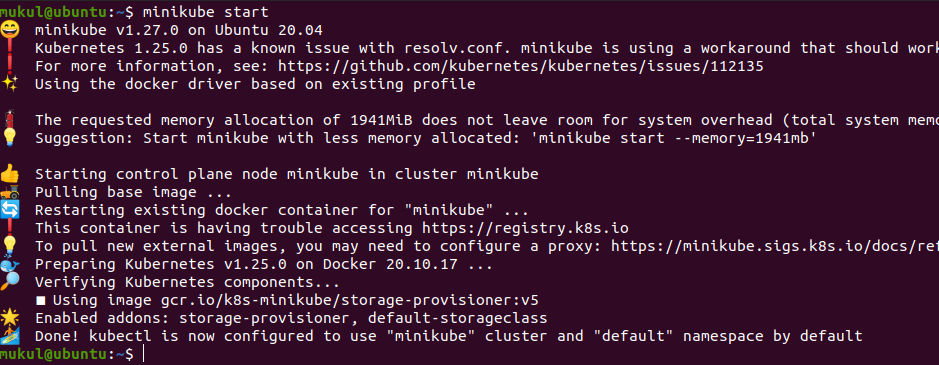
Start the minikube software with the following command:
minikube start
On running the above command minikube start, Minikube start the program and set up the single node kubernetes cluster, the below screenshot shows its execution flow.
Step 2
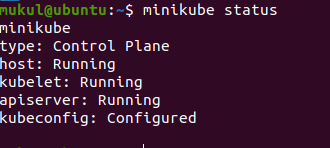
Verify whether the minikube is running or not with the following command minikube status
minikube status
Now we have to deploy a pod, we are going to use a pod that will be running an image of NGINX inside it.
Step 3
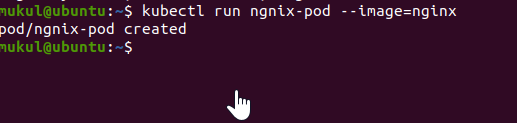
Run the kubernetes pod on using nginx image with the kubectl run command as shown below:
kubectl run <pod_name> --image=<your_image_name>
On Running the above command, kubectl will create a pod with nginx image extracting from the Docker hub. You can see its creation as a result after running the command on the below screenshot.
The above command will create a pod inside your minikube.
Step 4
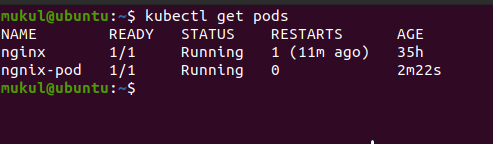
For viewing, list the all pods in the default namespace by the following command:
kubectl get pods
The above command list out the all the pods in the kubernetes, with the can know the status of your created pod and its age of creation. The below screenshot illustrates it clearly.
Now that our pod is created, let us enter inside our pod and run some commands.
Step 5
Connecting to the Minikube environment with ssh protocol by using the following command:
minikube ssh
On Executing this command, It will help you to land in minikube interactive environment from your local environment. You can understand it from seeing the hostnames in the below screenshot.
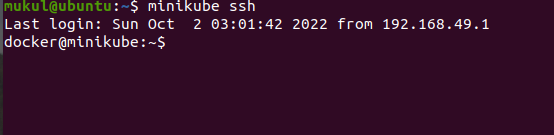
Step 6
Check the list of all the running containers inside the Minikube environment with the following command.
docker ps -a
The above command list out with displaying all the containers that are created with kubectl from local environment to the Minikube.
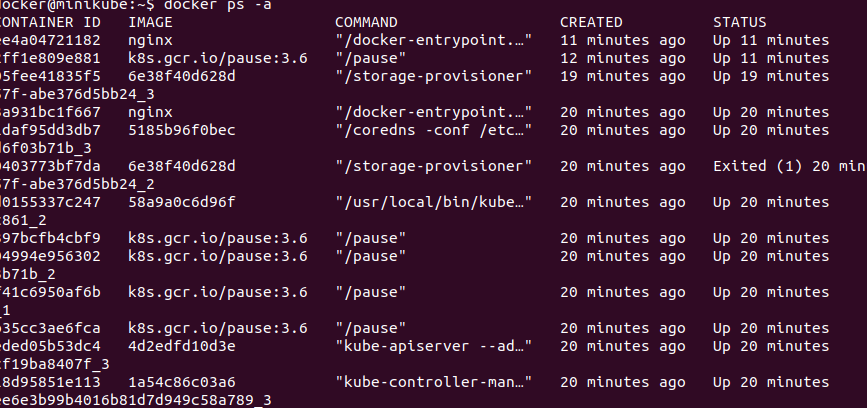
From here we will get access to inside the Nginx-pod and run some commands with the following steps.
Step 7
Get inside the nginx pod container with its container_name or container_id knowing from the above step command docker ps -a. The following command helps you in going inside the nginx pod container.
docker exec -it <Id_of_container> /bin/bash
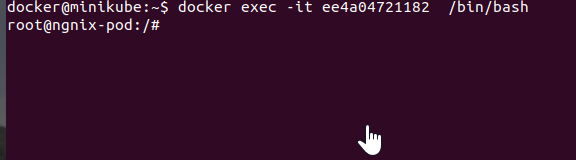
Now we are inside the Nginx-pod, let us run a few shell commands like ls, pwd, and cd.
Outputs Of Shell Commands Execution
With Step 7 you are landed to inside the pod container, from the can run the shell commands here the below screenshots shows its execution practically.
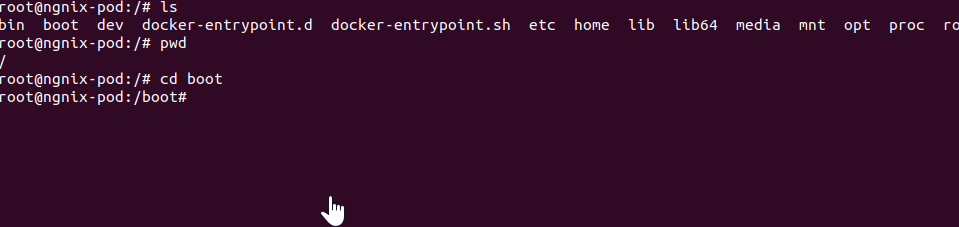
So, This is how we can use the minikube to deploy a pod and run a command inside it.
Best Practices Of Executing Shell Commands In Kubernetes
-
Use {kubectl exec} With Precision: Making sure that the
kubectl execcommand is performed in the appropriate environment by specifying the target pod and container. -
Make Use Of The {-c} Flag For Multi-Container Pods: For accessing the shell of a particular container inside the pod, try to use the -c flag together with the
kubectl execcommand. -
Sequential Execution With
&&Operator: For executing multiple commands sequentially within a Kubernetes container using the&&Operator. It helps in maintaining a clear and efficient workflow. -
Debugging With
kubectl debug: This commandkubectl debugfacilitates starting the debugging session inside an active pod for troubleshooting and debugging purposes. It offers a wide setting for research and problem-solving. -
Non-Interactive Commands With Flags: For using one-off non-interactive commands try on using the
kubectl execalong with–stdin=falseand–tty=falseflags. It helps in the execution of commands without entering the Pod Internally providing enhanced automation and scripting capabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Learning how to run shell commands inside of Kubernetes Pods is helps in effectively managing the containerized applications. As discussed above within the Minikube Setup, users can easily deploy, manage, and debug their apps with more effectiveness. Through this way, developers can confidently engage with their Kubernetes environments. With this learning, running the shell commands you can enhance agility of software development and administration sections.